In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl (C=O) groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical (dialdehydes, diketones, diesters, etc.) or unsymmetrical (keto-esters, keto-acids, etc.).
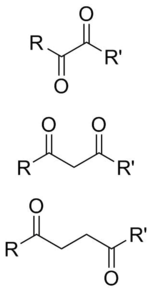
1,2-Dicarbonyls
edit1,2-Dialdehyde
editThe only 1,2-dialdehyde is glyoxal, (CHO)2. Like many alkyldialdehydes, glyoxal is encountered almost exclusively as its hydrate and oligomers thereof. These derivatives often behave equivalently to the aldehydes since hydration is reversible. Glyoxal condenses readily with amines. Via such reactions, it is a precursor to many heterocycles, e.g. imidazoles.
1,2-Diketones
editThe principal diketone is diacetyl, also known as 2,3-butanedione, CH3C(O)C(O)CH3. 1,2-Diketones are often generated by oxidation (dehydrogenation) of the diols:[1]
2,3-Butanedione, 2,3-pentanedione, and 2,3-hexanedione are found in small amounts in various foods. They are used as aroma components in alcohol-free beverages and in baked goods.[1] Benzil, (PhCO)2, is the corresponding diphenyl derivative.
A distinctive feature of 1,2-diketones is the long C-C bond linking the carbonyl groups. This bond distance is about 1.54 Å, compared to 1.45 Å for the corresponding bond in 1,3-butadiene. The effect is attributed to repulsion between the partial positive charges of the carbonyl carbon atoms.[2]
1,2-Diketones condense with many bifunctional nucleophiles, such as urea and thiourea to give heterocycles. Condensation with aromatic amines gives diketimine ((RC=NAr)2).
In the cases of 1,2-cyclohexanedione and 1,2-cyclopentanedione, the enol is about 1-3 kcal/mol more stable than the diketo form.[3]
ortho-Quinone, C4H4(CO)2, is the parent of a large family of 1,2-diketones.
1,2-Ketoaldehydes
editA well-known compound of this class is methylglyoxal, CH3C(O)CHO, also known as pyruvaldehyde. These compounds are also known as 2-oxoaldehydes[4] or α-ketoaldehydes.
1,2-Diesters and diacids
editOxalic acid and its esters define this family of compounds. The diacid is produced industrially by oxidation of waste sugars. It occurs naturally (as the conjugate base), notably in members of the plant species Oxalis. Condensation of the diesters with diamines gives cyclic diamides.
α-Keto- and formylcarboxylic acids
editα-Keto-acids and -esters are well known. Pyruvic acid (CH3C(O)CO2H) is the parent α-ketoacid. Its conjugate base, pyruvate (CH3C(O)CO−2), is a component of the citric acid cycle and product of glucose metabolism (glycolysis). The corresponding aldehyde-acid is glyoxalic acid (HC(O)CO2H).
1,3-Dicarbonyls
edit1,3-Dialdehydes
editThe parent 1,3-dialdehyde is malondialdehyde (CH2(CHO)2), a β-dicarbonyl. Like most dialdehydes, it is rarely encountered as such. Instead it is handled almost exclusively as its hydrate, methyl acetal, and oligomers thereof. These derivatives often behave like the parent. Many 2-substituted derivatives are known. They are often prepared by alkylation of the enolate of malondialdehyde.
1,3-Diketones
edit1,3-Diketones are also called β-diketones. An important member is acetylacetone, CH3C(O)CH2C(O)CH3. Dimedone is a cyclic 1,3-diketone. 1,3-Indandione is the cyclic 1,3-diketone fused to a benzene ring. Acetylacetone is prepared industrially by the thermal rearrangement of isopropenylacetate.[1] Another cyclic 1,3-diketone is 2,2,4,4-tetramethylcyclobutanedione, which is a precursor to a useful diol.
1,3-Diketones often tautomerize to an enol and ketol. They usually exist predominantly in the enol form [citation needed]. The percent enol in acetylacetone, trifluoroacetylacetone, and hexafluoroacetylacetone are 85, 97, and 100%, respectively (neat, 33 °C).[5] Cyclic 1,3-diketones, such as 1,3-cyclohexanedione and dimedone, similarly exist significantly in the enol form.
Like other diketones, 1,3-diketones are versatile precursors to heterocycles. The conjugate base derived from 1,3-ketones can serve as ligand s to form metal acetylacetonate coordination complexes. In the DeMayo reaction 1,3-diketones react with alkenes in a photochemical pericyclic reaction to form (substituted) 1,5-diketones.
Classically, 1,3-diketones are prepared by the Claisen condensation of a ketone with an ester.
1,3-Diesters and diacids
editMalonic acid and its esters are the parent members of this class of dicarbonyls. Also common are the 2-substituted derivatives with the formula RCH(CO2R)2, which arise by C-alkylation of the conjugate base (the enolate) NaCH(CO2R)2.
β-Keto-esters
editβ-Keto-esters arise readily by the condensation of a pair of esters. A well known example is ethyl acetoacetate (although it is prepared by ethanolysis of ketene).
1,4-Dicarbonyls
edit1,4-Dialdehydes
editSuccinaldehyde (CH2CHO)2 is the simplest and parent 1,4-dialdehyde. The aromatic derivative is phthalaldehyde.
1,4-Diketones
editDiketones with two methylene groups separating the carbonyl groups, also called γ-diketones, typically coexist with their enol tautomers. The preeminent member is acetonylacetone. 1,4-Diketones are useful precursors to heterocycles via the Paal–Knorr synthesis, which gives pyrroles:
This reactivity is the basis of the neurotoxicity of γ-diketones.[6] 1,4-Diketones are also precursor to furans and thiophenes. The condensation of 1,4-diketones (and related substrates) with hydrazines afford dihydropyridazines, which can be converted to pyridazines.
para-quinone, C4H4(CO)2, is the parent of a large family of 1,4-diketones.
1,4-Diesters and diacids
editSuccinic acid and its esters are the parent members of this family of 1,4-dicarbonyls. Succinic acid is notable as a component in the citric acid cycle. It forms a cyclic acid anhydride, succinic anhydride. Unsaturated members include maleic and fumaric acids and their esters.
1,5-Dicarbonyls
edit1,5-Dialdehydes
editGlutaraldehyde (CH2)3(CHO)2 is the simplest and parent 1,5-dialdehyde. It hydrates readily. The aromatic analogue is isophthalaldehyde.[7]
1,5-Diketones
editThese diketones have three methylene groups separating the carbonyl groups.
1,5-Diesters and diacids
editGlutaric acid (CH2)3(CO2H)2 is the parent 1,5-diacid.
Hydration and cyclization
editSmall aldehydes tend to hydrate. Hydration is prevalent for dialdehydes. Glyoxal forms a series of cyclic hydrates. Succinaldehyde hydrates readily to give 2,5-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran. The aromatic phthalaldehyde also forms hydrated.
Similar hydration and cyclization equilibria apply to maleic dialdehyde,[8][9] glutaraldehyde, and adipaldehyde.
Safety
editA number of dicarbonyl compounds are bioactive. Diacetyl is known to cause the lung disease bronchiolitis obliterans in those individuals exposed to it in an occupational setting.[10] Dialdehydes, e.g. glutaraldehyde and malonaldehyde, are fixatives or sterilizers.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c Hardo Siegel; Manfred Eggersdorfer (2007). "Ketones". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. p. 16. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_077. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Eriks, K.; Hayden, T. D.; Yang, S. Hsi; Chan, I. Y. (1983). "Crystal and molecular structure of biacetyl (2,3-butanedione), (H3CCO)2, at -12 and -100 °C". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105 (12): 3940–3942. doi:10.1021/ja00350a032.
- ^ Jana, Kalyanashis; Ganguly, Bishwajit (2018). "DFT Study to Explore the Importance of Ring Size and Effect of Solvents on the Keto–Enol Tautomerization Process of α- and β-Cyclodiones". ACS Omega. 3 (7): 8429–8439. doi:10.1021/acsomega.8b01008. PMC 6644555. PMID 31458971.
- ^ "CHEBI:27659 - 2-oxo aldehyde". Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI).
- ^ Jane L. Burdett; Max T. Rogers (1964). "Keto-Enol Tautomerism in β-Dicarbonyls Studied by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. I. Proton Chemical Shifts and Equilibrium Constants of Pure Compounds". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86: 2105–2109. doi:10.1021/ja01065a003.
- ^ Stephen R Clough; Leyna Mulholland (2005), "Hexane", Encyclopedia of Toxicology, vol. 2 (2nd ed.), Elsevier, pp. 522–525
- ^ Ackerman, J. H.; Surrey, A. R. (1967). "Isophthalaldehyde". Organic Syntheses. 47: 76. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.047.0076.
- ^ Hardy, P. M.; Nicholls, A. C.; Rydon, H. N. (1972). "The Hydration and Polymerisation of Succinaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde, and Adipaldehyde". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 2 (15): 2270. doi:10.1039/P29720002270.
- ^ D. M. Burness (1960). "2,5-Dihydro-2,5-Dimethoxyfuran". Organic Syntheses. 40: 29. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.040.0029.
- ^ Kreiss, Kathleen (August 2017). "Recognizing occupational effects of diacetyl: What can we learn from this history?". Toxicology. 388: 48–54. Bibcode:2017Toxgy.388...48K. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2016.06.009. PMC 5323392. PMID 27326900.