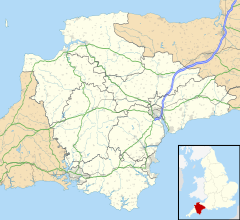
Dartmouth (/ˈdɑːrtməθ/) is a town and civil parish in the English county of Devon. It is a tourist destination set on the western bank of the estuary of the River Dart, which is a long narrow tidal ria that runs inland as far as Totnes. It lies within the South Devon Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and South Hams district, and had a population of 5,512 in 2001,[1] reducing to 5,064 at the 2011 census.[2] There are two electoral wards in the Dartmouth area (Townstal & Kingswear). Their combined population at the above census was 6,822.[3][4]
| Dartmouth | |
|---|---|
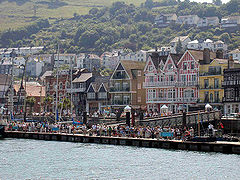 Dartmouth from the River Dart | |
Location within Devon | |
| Population | 5,064 (2011) |
| OS grid reference | SX877514 |
| Civil parish |
|
| District | |
| Shire county | |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | DARTMOUTH |
| Postcode district | TQ6 |
| Dialling code | 01803 |
| Police | Devon and Cornwall |
| Fire | Devon and Somerset |
| Ambulance | South Western |
| UK Parliament | |
History
editIn 1086, the Domesday Book listed Dunestal as the only settlement in the area which now makes up the parish of Dartmouth. It was held by Walter of Douai. It paid tax on half a hide, and had two plough teams, two slaves, five villagers and four smallholders. There were six cattle, 40 sheep and 15 goats. At this time Townstal (as the name became) was apparently a purely agricultural settlement, centred around the church. Walter of Douai rebelled against William II, and his lands were confiscated and added to the Honour of Marshwood (Dorset), which sublet Townstal and Dartmouth to the FitzStephens.[5] It was probably during the early part of their proprietorship that Dartmouth began to grow as a port, as it was of strategic importance as a deep-water port for sailing vessels. The port was used as the sailing point for the Crusades of 1147 and 1190, and Warfleet Creek, close to Dartmouth Castle is supposed by some to be named for the vast fleets which assembled there.[6] Dartmouth was a home of the Royal Navy from the reign of Edward III and was twice surprised and sacked during the Hundred Years' War, after which the mouth of the estuary was closed every night with a great chain. The narrow mouth of the Dart is protected by two fortified castles, Dartmouth Castle and Kingswear Castle. Originally Dartmouth's only wharf was Bayard's Cove, a relatively small area protected by a fort at the southern end of the town.
In 1373 Geoffrey Chaucer visited and among the pilgrims in his Canterbury Tales,
A schipman was ther, wonyng fer by weste;
For ought I wost, he was of Dertemouthe.
Notwithstanding Dartmouth's connections with the crown and respectable society, it was a major base for privateering in medieval times. John Hawley or Hauley, a licensed privateer and sometime mayor of Dartmouth is reputed to be a model for Chaucer's "schipman".[7][8]
The earliest street in Dartmouth to be recorded by name (in the 13th century) is Smith Street. Several of the houses on the street are originally late 16th century or early 17th century and probably rebuilt on the site of earlier medieval dwellings. The street name undoubtedly derives from the smiths and shipwrights who built and repaired ships here when the tidal waters reached as far as this point. Smith Street was also the site of the town pillory in medieval times.
The first church in the parish was St Clement's, Townstal, which may have existed in some form before the 1190s. It was granted by the FitzStephens to Torre Abbey in about 1198, the Abbey having been founded in 1196, and the present stone-built church was probably started shortly after this.[9]
Manorial transactions are first recorded in 1220, when the manor house was at Norton, about half a mile west of Townstal. Names of occupations also started to appear, including taverner, tailor, coggar, korker, goldsmith, glover, skinner and baker. The "Fosse", now Foss Street, a dam across the creek known later as The Mill Pool, was first mentioned in 1243. The flow of water out of the pool through the Mill Gullet powered a tidal mill. The dam was used as an unofficial footpath linking Clifton, to the south, with Hardness, to the north. Before this it was necessary to go westwards to the head of the creek at Ford to travel between the two settlements. The lord of the manor was given the rights to hold a weekly market and an annual fair in 1231. In 1281, a legal case proved that the Lord of Totnes had the right to charge tolls on ships using the river, and this right was bought by Nicholas of Tewkesbury in 1306, who conveyed the town, river and port to the king in 1327, so making Dartmouth a Royal Borough. The king gave the river to the Duchy of Cornwall in 1333, who still own the "fundus" or bed of the river.[10] In 1335 Edward III granted Dartmouth to Joan of Carew, whose husband was Lord of Stoke Fleming, and almost immediately she obediently passed the lordship to Guy de Bryan, one of the king's leading ministers. In 1341, the town was granted a Royal Charter, which allowed for the election of a mayor. The borough was required to provide two ships for forty days per year. After 1390, no more is heard of lordship rights, and the borough became effectively independent of any lord.
St Saviour's Church was constructed in 1335 and consecrated in 1372. It contains a pre-Reformation oak rood screen built in 1480 and several monuments including the tomb of John Hawley (died 1408) and his two wives, covered with a large brass plate effigy of all three. A large medieval ironwork door is decorated with two leopards of the Plantagenets and is possibly the original portal. Although it is dated "1631", this is thought to be the date of a subsequent refurbishment coincidental with major renovations of the church in the 17th century.[11] The gallery of the church is decorated with the heraldic crests of prominent local families and is reputed to be constructed of timbers from ships captured during the defeat of the Spanish Armada,[12] although this has not been categorically substantiated. An engraving of a painting by Thomas Allom of the interior of the church, showing the rood screen, provided the inspiration for Letitia Elizabeth Landon's poetical illustration Dartmouth Church in Fisher's Drawing Room scrap Book, 1833.[13]
In medieval times, land access from the Totnes direction passed the manor at Norton and the parish church at Townstal before falling steeply along what are now Church Road, Mount Boone and Ridge Hill to the river at Hardness. There were steeper routes via Townstal Hill and Clarence Street and also via Brown's Hill. These were all too steep for vehicles, so the only land access was by packhorse. In 1671 there is the first mention of the building of the "New Ground". A previously existing sandbank was built up using ships' ballast, and a quay wall was built around it to provide more mooring space. The area proved too unstable to be built on, and is now the Royal Avenue Gardens. It was originally linked to the corner of the Quay by a bridge, opposite Duke Street. At the other end of The Quay, Spithead extended into the river for a few yards.
Dartmouth sent numerous ships to join the English fleet that attacked the Spanish Armada, including the Roebuck, Crescent and Hart.[14] The Nuestra Señora del Rosario, the Spanish Armada's "payship" commanded by Admiral Pedro de Valdés, was captured along with all its crew by Sir Francis Drake. It was reportedly anchored in the River Dart for more than a year and the crew were used as labourers on the nearby Greenway Estate which was the home of Sir Humphrey Gilbert and his half-brother Sir Walter Raleigh. Greenway was later the home of Dame Agatha Christie.[15]
In 1592 the Madre de Deus, a Portuguese treasure ship captured by the English in the Azores, docked at Dartmouth Harbour. It attracted all manner of traders, dealers, cutpurses and thieves and by the time Sir Walter Raleigh arrived to reclaim the Crown's share of the loot, a cargo estimated at half a million pounds had been reduced to £140,000.[16] Still, ten freighters were needed to carry the treasure to London.
Henry Hudson put into Dartmouth on his return from North America, and was arrested for sailing under a foreign flag. The Pilgrim Fathers put into Dartmouth's Bayard's Cove, en route from Southampton to America. They rested a while before setting off on their journey in the Mayflower and the Speedwell on 20 August 1620. About 300 miles west of Land's End, upon realising that the Speedwell was unseaworthy, it returned to Plymouth. The Mayflower departed alone to complete the crossing to Cape Cod. Dartmouth's sister city is Dartmouth, Massachusetts.
The town contains many medieval and Elizabethan streetscapes and is a patchwork of narrow lanes and stone stairways. A significant number of the historic buildings are listed.[17] One of the most obvious is the Butterwalk, built 1635 to 1640. Its intricately carved wooden fascia is supported on granite columns. Charles II held court in the Butterwalk whilst sheltering from storms in 1671 in a room which now forms part of Dartmouth Museum.[18] Much of the interior survives from that time.
The Royal Castle Hotel was built in 1639 on the then new quay. The building was re-fronted in the 19th century, and as the new frontage is itself listed, it is not possible to see the original which lies beneath. A claimant for the oldest building is a former merchant's house in Higher Street, now a Good Beer Guide listed public house called the Cherub, built circa 1380. Agincourt House (next to the Lower Ferry) is also 14th century.
The remains of a fort at Gallants Bower just outside the town are some of the best preserved remains of a Civil War defensive structure.[19] The fort was built by Royalist occupation forces in c. 1643 to the south east of the town, with a similar fort at Mount Ridley on the opposite slopes of what is now Kingswear. The Parliamentarian General Fairfax attacked from the north in 1646, taking the town and forcing the Royalists to surrender, after which Gallants Bower was demolished.
19th century
editBefore 1671, what is now the town centre was almost entirely tidal mud flats. The New Road (now Victoria Road) was constructed across the bed of the (silted up) Mill Pool and up the Ford valley after 1823. Spithead was extended in 1864 when the Dartmouth and Torbay Railway arrived in Kingswear and a pontoon was constructed, linked to Spithead by a bridge. The railway directors and others formed the Dartmouth Harbour Commissioners. At this time, all the roads in those parts of Dartmouth which were not land reclamations were very narrow. In 1864-7 Higher Street was widened into Southtown and linked to Lower Street, which was also widened, with the northern part renamed Fairfax Place. Some of the buildings were rebuilt further back with decorative frontages. In 1881 the Harbour Commissioners produced a scheme for an embankment or esplanade from near the Lower Ferry to Hardness, across the remains of The Pool, to provide an attraction for tourists and further mooring space. It was completed in 1885 after much disagreement between the Borough, the Commissioners and the Railway (now the Great Western Railway). A new station was also built at this time.[20][21] The building of the Embankment left a section of river isolated between Spithead and the New Ground, which is known as The Boatfloat, and is linked to the river by a bridge for small vessels under the road.
The coming of steam ships led to Dartmouth being used as a bunkering port, with coal being brought in by ship or train. Coal lumpers were members of gangs, who competed to bunker the ships by racing to be first to a ship. This led to the men living as close as possible to the river, and their tenements became grossly overcrowded, with the families living in slum conditions, with up to 15 families in one house, one family to a room.[22]
The Royal National Lifeboat Institution opened the Dart Lifeboat Station at the Sand Quay in 1878, but it was closed in 1896. In all this time only one effective rescue was made by the lifeboat.[23]
20th century
editThe area to the north of Ridge Hill was a shallow and muddy bay ("Coombe Mud") with a narrow road running along the shore linking with the Higher Ferry. The mud was a dumping ground for vessels, including a submarine. The reclamation was completed in 1937 by the extension of the Embankment and the reclamation of the mud behind it, which became Coronation Park.
In the 1920s, aided by government grants, the council made a start on clearing the slums. This was aided by the decline in the use of coal as a fuel for ships. The slums were demolished, and the inhabitants were rehoused in new houses in the Britannia Avenue area, to the west of the old village or hamlet of Townstal. The process was interrupted by the second world war, but was resumed with the construction of many prefabs, and later more houses. Community facilities were minimal at first, but a central area was reserved for a church, which was used by the Baptists and opened in 1954,[24] together with a speedway track. The latter was later used for housing, but a new community centre was opened nearby,[25] together with a leisure centre, an outdoor swimming pool, and later an indoor pool,[26] and supermarkets. There are also light industrial units.
In the latter part of the Second World War the town was a base for American forces and one of the departure points for Utah Beach in the D Day landings. Slipways and harbour improvements were also constructed. Much of the surrounding countryside and notably Slapton Sands was closed to the public while it was used by US troops for practise landings and manoeuvres. Between 1985 and 1990 the Embankment was widened by 6 metres and raised to prevent flooding at spring tides. A tidal lock gate was provided at the Boatfloat bridge, which could be closed at such times.
21st century
editDart Lifeboat Station was reopened in 2007, the first time that a lifeboat had been stationed in the town since 1896. It has initially been kept in a temporary building in Coronation Park.[23]
In 2010, a fire seriously damaged numerous historical properties in Fairfax Place and Higher Street. Several were Tudor and Grade I or Grade II listed buildings.[27]
Governance
editThe town was an ancient borough, incorporated by Edward III, known formally as Clifton-Dartmouth-Hardness, and consisting of the three parishes of St Petrox, St Saviour and Townstal, and incorporating the hamlets of Ford, Old Mill and Norton.[28] It was reformed under the Municipal Corporations Act 1835. The town returned two members of parliament from the 13th century until 1835, after which one Member of Parliament (MP) was elected until the town was disenfranchised in 1868. It remained a municipal borough until 1974, when it was merged into the South Hams district, and became a successor parish of Dartmouth with a town council.[29][30]
Dartmouth Town Council is the lowest of three tiers of local government. It consists of 16 councillors representing the two wards of Clifton and Townstal.[31] At the second tier, Dartmouth forms part of the Dartmouth and Kingswear ward of South Hams District Council, which returns three councillors.[32] At the upper tier of local government Dartmouth and Kingswear Electoral Division elects one member to Devon County Council.[33]
Culture and tourism
editThe Port of Dartmouth Royal Regatta takes place annually over three days at the end of August. The event sees the traditional regatta boat races along with markets, fun fairs, community games, musical performances, air displays including the Red Arrows and fireworks. A Royal Navy guard ship is often present at the event. Other cultural events include beer festivals in February and July (the latter in Kingswear), a music festival and an art and craft weekend in June, a food festival in October and a Christmas candlelit event.[34]
The Flavel Centre incorporates the public library and performance spaces, featuring films, live music and comedy and exhibitions.[35]
Bayard's Cove has been used in several television productions, including The Onedin Line[36] a popular BBC television drama series that ran from 1971 to 1980. Many of the scenes from the BBC's popular series Down to Earth, starring Ricky Tomlinson, were filmed at various locations around the town.[37]
Notable tourist attractions include the Dartmouth Royal Naval College, Bayard's Cove Fort, Dartmouth Castle and the Dartmouth Steam Railway which terminates at Kingswear on the opposite bank of the river.
Boat cruises to nearby places along the coast (such as Torbay and Start Bay) and up the river (to Totnes, Dittisham and the Greenway Estate) are provided by several companies. The paddlesteamer PS Kingswear Castle returned to the town in 2013.[38] The South West Coast Path National Trail passes through the town, and also through extensive National Trust coastal properties at Little Dartmouth and Brownstone (Kingswear). The Dart Valley Trail starts in Dartmouth, with routes either side of the River Dart as far as Dittisham, and continuing to Totnes via Cornworthy, Tuckenhay and Ashprington. The area has long been well regarded for yachting, and there are extensive marinas at Sandquay, Kingswear and Noss (approximately one mile north of Kingswear).
Climate
editThe nearest Met Office weather station is Slapton, about 5 miles south-south west of Dartmouth and a similar distance from the coast. As with the rest of the British Isles and South West England, the area experiences a maritime climate with warm summers and mild winters—this is particularly pronounced due to its position near the coast—extremes range from a record low of just −8.0 °C (17.6 °F) in January 1987[39] up to a record high of 30.5 °C (86.9 °F) during June 1976.[40]
| Climate data for Slapton, elevation: 32 m (105 ft), 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1960–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.6 (58.3) |
16.2 (61.2) |
19.5 (67.1) |
20.5 (68.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
30.5 (86.9) |
28.0 (82.4) |
28.5 (83.3) |
25.0 (77.0) |
21.9 (71.4) |
17.7 (63.9) |
15.7 (60.3) |
30.5 (86.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.2 (48.6) |
9.1 (48.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
12.8 (55.0) |
15.7 (60.3) |
18.6 (65.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.7 (69.3) |
18.5 (65.3) |
15.2 (59.4) |
12.0 (53.6) |
9.8 (49.6) |
14.5 (58.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.5 (43.7) |
6.3 (43.3) |
7.8 (46.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
12.1 (53.8) |
14.6 (58.3) |
16.8 (62.2) |
16.9 (62.4) |
15.0 (59.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
9.2 (48.6) |
7.1 (44.8) |
11.1 (52.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 3.8 (38.8) |
3.5 (38.3) |
4.8 (40.6) |
5.6 (42.1) |
8.4 (47.1) |
10.6 (51.1) |
12.8 (55.0) |
13.0 (55.4) |
11.4 (52.5) |
9.3 (48.7) |
6.4 (43.5) |
4.4 (39.9) |
7.9 (46.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.0 (17.6) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
2.5 (36.5) |
6.2 (43.2) |
6.0 (42.8) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.2 (32.4) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 123.5 (4.86) |
94.0 (3.70) |
90.0 (3.54) |
70.4 (2.77) |
67.0 (2.64) |
60.9 (2.40) |
63.8 (2.51) |
66.1 (2.60) |
71.9 (2.83) |
114.3 (4.50) |
118.6 (4.67) |
133.5 (5.26) |
1,074 (42.28) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 14.7 | 11.5 | 12.7 | 10.5 | 9.9 | 8.2 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 13.7 | 14.5 | 14.6 | 137.7 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 57.5 | 76.4 | 118.5 | 180.7 | 210.7 | 213.9 | 215.6 | 198.0 | 154.9 | 102.3 | 74.8 | 48.3 | 1,651.6 |
| Source 1: Met Office[41] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: KNMI[42] | |||||||||||||
Transport
editDartmouth is linked to Kingswear, on the other side of the River Dart, by three ferries. The Higher Ferry and the Lower Ferry are both vehicular ferries. The Passenger Ferry, as its name suggests, carries only passengers, principally to connect with the Dartmouth Steam Railway at Kingswear railway station. The nearest bridge across the Dart is in Totnes, some 11 miles (18 km) away by road.[43]
The A379 road runs through Dartmouth, linking the town to Slapton and Kingsbridge to the southwest and to Torbay to the east across the Higher Ferry. The A3122 connects Dartmouth to a junction with the A381, and hence to both Totnes and a more direct route to Kingsbridge. Stagecoach South West provides local town bus services and links to Plymouth, Totnes and Exeter, and Kingsbridge. In addition it provides links to the Torbay resorts of Brixham, Paignton and Torquay from Kingswear via the ferry.
No railway has ever run to Dartmouth, but the town does have a railway station,[44] opened on 31 March 1890 to replace the original facility on the pontoon,[45] although it is now a restaurant. In fact Dartmouth Railway Station was built while the line from Paignton to the River Dart was still being built, anticipating a bridge across the river being built near the present Greenway Halt. The railway line to Kingswear was opened in 1864. As a result of shortage of capital, a deviation from the original scheme to run the line from Churston to Greenway with a steamer service to Dartmouth was proposed, but defeated in Parliament. It had been suggested that this could, at a later date, be used as a jumping off point for a bridge to the west bank of the Dart and a line direct to Dartmouth.[46] In 1900, a Light Railway scheme was proposed for a crossing of the Dart near Maypool to join another line from Totnes and then proceed to Kingsbridge and Yealmpton, with a branch to Salcombe.[47] This was also defeated by lack of funds. The railway terminated at a station called "Kingswear for Dartmouth" (now on the Dartmouth Steam Railway) and a ferry took passengers across the river to the station at Dartmouth railway station, which had a dedicated pontoon. British Railways formally closed the line to mainline passenger trains in 1973, but it immediately re-opened as a heritage line and has run as one ever since.
Media
editLocal TV coverage is provided by BBC West and ITV West Country. Television signals are received from the Beacon Hill TV transmitter and the local relay transmitter situated south east of the town.[48]
Local radio stations include BBC Radio Devon on 104.3 FM, Heart West on 96.4 FM, Greatest Hits Radio South Devon on 105.5 FM, and Radio Exe on 107.3 FM.
The Dartmouth Chronicle is the town's local weekly newspaper.
Education
editBritannia Royal Naval College
editThe town is home to the Royal Navy's officer training college (Britannia Royal Naval College), where all officers of the Royal Navy and many foreign naval officers are trained.
Schools
editDartmouth has one primary school—St John the Baptist R.C. Primary School, and one all-through school—Dartmouth Academy—for those aged 3–16. Dartmouth also has a pre-school in the centre of town, established for over 40 years and based in the old Victorian school rooms at South Ford Road. It provides care for 2- to 5-year-olds and is run as a charitable organisation.
Sport and leisure
editDartmouth has a Non-League football club Dartmouth A.F.C. who play at Long Cross.
Dartmouth also hosts the annual "World Indoor Rally Championship", based on slot car racing in the late summer.[49][50]
At the end of August and early September there is the annual Port of Dartmouth Royal Regatta.
Since 1905 Dartmouth has had a greenhouse as part of the Royal Avenue Gardens.[51][52] In May 2013 this building, used for the previous 10 years by Dartmouth in Bloom,[53] a not-for-profit organisation affiliated with Britain in Bloom, was closed as structurally unsound.[54] There are proposals to restore the greenhouse to its prior Edwardian style.[55]
Notable residents
edit- George Parker Bidder (1806–1878), the civil engineer and calculating prodigy, notable for his work on railways over much of the world, as well as the docks of the East End in the Port of London. Bidder died at his home at Paradise Point near Warfleet Creek and is buried at nearby Stoke Fleming.
- Simon Drew (born 1952), a commercially successful cartoonist and illustrator, lives in Dartmouth and runs a shop on Fosse Street.
- John Flavel (ca.1627–1691), an English Puritan Presbyterian minister and author.
- Gordon Onslow Ford (1912–2003), a leading British surrealist painter, attended the Royal Naval College.
- Sir John Harvey Jones (1924–2008), businessman and television presenter, attended the Royal Naval College.
- Rachel Kempson (1910–2003), stage and film actress, was born in Dartmouth. She was the wife of Sir Michael Redgrave and mother of Vanessa, Lynn and Corin, and published her autobiography, Life Among the Redgraves, in 1988.
- Christopher Robin Milne (1920–1996), son of A. A. Milne, after whom the character Christopher Robin in the Winnie-the-Pooh books was named, used to own the Harbour Bookshop. The bookshop closed in September 2011.[56]
- Thomas Newcomen (1664–1729), the inventor of the atmospheric engine – the first successful steam-powered pumping engine—was born in Dartmouth in 1663. An 18th-century working Newcomen steam engine is on display in the town.[57]
- Sir Nicholas Harris Nicolas (1799–1848), an English antiquary.[58]
- Mary Nightingale (born 1963), ITV newscaster, lived in Dartmouth for much of her childhood.
- John "Jack" Russell (1795–1883), an English parson, an enthusiastic fox-hunter and dog breeder.[59]
- Flora Thompson (1876–1947), lived in Above Town between 1928 and 1940, writing Lark Rise and Over to Candleford during this time. The books were later published as Lark Rise to Candleford. She is buried at Longcross Cemetery.
- Theodore Veale (1892–1980), recipient of the Victoria Cross during the First World War.
- John L. Wimbush (1854–1914), landscape and portrait painter.
- Stephen Beresford, BAFTA winning screenwriter and playwright grew up in the town and has written several plays set in Dartmouth, including The Last of the Haussmans first performed at the Royal National Theatre.
References
edit- ^ Office for National Statistics : Census 2001 : Parish Headcounts : South Hams Archived 12 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 27 January 2010
- ^ "Parish population 2011". Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Dartmouth and Kingswear ward 2011". Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Dartmouth Townstall ward 2011". Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ Freeman, Ray (1990). Dartmouth and its Neighbours 1st Ed. Chichester: Phillimore. pp. 17–18. ISBN 0-85033-697-X.
- ^ "What's in A Name – Warfleet Creek". By The Dart. 2 June 2016. Archived from the original on 18 November 2022. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- ^ "John Hawley of Dartmouth". Devonperspectives.co.uk. 11 February 2012. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ "Roll of Mayoralty". Dartmouth-history.org.uk. Archived from the original on 29 February 2012. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ Freeman, Ray (1990). Dartmouth and its Neighbours (1st ed.). Chichester: Phillimore. pp. 19–21. ISBN 0-85033-697-X.
- ^ Freeman, Ray (1990). Dartmouth and its Neighbours (1 ed.). Chichester: Phillimore. pp. 23–24. ISBN 0-85033-697-X.
- ^ "St Saviour, Dartmouth, Devon – Church". Roughwood.net. 27 February 2009. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ Andrews, Robert (2013). The Rough Guide to Devon & Cornwall. Rough Guides UK. ISBN 9781409364863.
- ^ Landon, Letitia Elizabeth (1832). "picture". Fisher's Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1833. Fisher, Son & Co.Landon, Letitia Elizabeth (1832). "poetical illustration". Fisher's Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1833. Fisher, Son & Co.
- ^ Russell, Percy (September 1946). Ancient Dartmouth (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 February 2012. Retrieved 2 February 2013.
- ^ "Dartmouth, Devon – Destinations UK". Historic-uk.com. 4 June 1944. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ McDermott, James (2001). Martin Frobisher: Elizabethan Privateer. Yale University Press. pp. 397–398. ISBN 9780300083804.
Dartmouth.
- ^ Good Stuff IT Services. "Listed Buildings in Dartmouth, Devon, England". British Listed Buildings. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ "The King's Room at Dartmouth Museum". Dartmouth Museum. Archived from the original on 17 July 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
It was in this magnificent room that King Charles II was entertained in July 1671, when storms forced him to seek shelter in Dartmouth.
- ^ "Gallants Bower". National Trust. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- ^ Freeman, Ray (1990). Dartmouth and its Neighbours. Chichester: Phillimore. pp. 166–168. ISBN 0-85033-697-X.
- ^ Potts, C.R. (2014). The Newton Abbot to Kingswear Railway (2 ed.). Usk: Oakwood Press. pp. 92, 335–339. ISBN 978-0-85361-733-4.
- ^ Freeman, Ray (1990). Dartmouth and its Neighbours. Chichester: Phillimore. pp. 178–180. ISBN 0-85033-697-X.
- ^ a b Leach, Nicholas (2009). Devon's Lifeboat Heritage. Chacewater: Twelveheads Press. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-0-906294-72-7.
- ^ "Dartmouth Baptist Church". Archived from the original on 8 April 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- ^ "Townstal Community Hall". By the Dart. Archived from the original on 18 November 2022. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- ^ "Dartmouth and District Indoor Pool". Archived from the original on 18 November 2022. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- ^ "Dartmouth's Tudor buildings destroyed by chip shop fire". BBC News. 29 May 2010. Retrieved 30 May 2010.
- ^ Pigot & Co.'s Devonshire (1830) Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine GenUKi
- ^ The English Non-metropolitan Districts (Definition) Order 1972 (S.I. 1972 No. 2039)
- ^ The Local Government (Successor Parishes) Order 1973 (S.I. 1973 No. 1110)
- ^ "Dartmouth Town Councillors, Dartmouth Town Council. Retrieved 21 March 2008".
- ^ "Election of District Councillors for Dartmouth and Kingswer" (PDF). South Hams District Council. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ^ "Division 36: Dartmouth and Kingswear, Devon County Council. Retrieved 21 March 2008". Archived from the original on 8 May 2005. Retrieved 21 March 2008.
- ^ "What's on in Dartmouth". Discover Dartmouth. Visit South Devon Community Interest Company. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- ^ "The Flavel Arts Centre & Cinema". Discover Dartmouth. Visit South Devon Community Interest Company. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- ^ "Things to Do – Indoor – Outdoor – Dartmouth Museum". Dartmouth Museum. Archived from the original on 10 July 2012. Retrieved 19 August 2011.
Bayards Cove was used in the BBC period drama The Onedin Line to represent the wharves and buildings of Liverpool Docks.
- ^ "Ricky Tomlinson on Bayard's Cove". Dartmouth dot TV. Archived from the original on 18 January 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- ^ "Paddlesteamer Kingswear Castle returns home to the Dart after 50 years". Western Morning News. 8 December 2012. Archived from the original on 5 May 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ "1987 temperature". KNMI.
- ^ "1976 temperature". KNMI. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- ^ "Slapton 1981–2010 averages". Met Office. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ^ "Indices data – Slapton station 1815". KNMI. Archived from the original on 9 July 2018. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ^ "Dart Harbour : Ferries". The Dart Harbour and Navigation Authority. Archived from the original on 19 October 2008. Retrieved 18 September 2008.
- ^ "Heritage, Landscape & Wildlife: Dartmouth Town Trail". South Devon AONB. Archived from the original on 26 February 2012. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ Potts, C.R. (2014). The Newton Abbot to Kingswear Railway (2nd ed.). Usk: Oakwood Press. p. 339. ISBN 978-0-85361-733-4.
- ^ Potts (2014), pp. 36–40
- ^ Williams and Reynolds, Ken and Dermot (1977). The Kingsbridge Branch. Oxford: Oxford Publishing Co. pp. 27, 28. ISBN 086093-001-7.
- ^ "Freeview Light on the Dartmouth (Devon, England) transmitter". UK Free TV. 1 May 2004. Retrieved 16 March 2024.
- ^ "World Indoor Rally Championship 2011". SlotForum International. 15 August 2012. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- ^ "WORLD CHAMPIONSHIP SCALEXTRIC RACE 2010 DARTMOUTH UK". Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 9 April 2018 – via YouTube.
- ^ "History of Dartmouth Community Greenhouse". Dartmouth in Bloom. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
The Dartmouth Greenhouse was built in 1905. This Greenhouse is part of the history of Royal Avenue Gardens and part of the heritage of the town of Dartmouth.
- ^ "Bloom team bid to restore greenhouse". North London Today. Tindle Newspapers. 15 March 2013. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
The greenhouse, built in 1905, was an original feature of the New Ground, which became Royal Avenue Gardens, and remains the oldest surviving feature of the gardens, six years older than the bandstand.
- ^ "Dartmouth in Bloom, horticultural achievement, environmental responsibility, community participation Dartmouth in Bloom". Dartmouth in Bloom. Retrieved 6 October 2013.
- ^ "Bloom contest fear over gardening cut". Dartmouth Chronicle. Tindle Newspapers. 3 May 2013. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
... the local bloom team has had to cope with the closure of its community Greenhouse which has been deemed too structurally dangerous to use.
- ^ "Bloom team bid to restore greenhouse". Dartmouth Chronicle. Tindle Newspapers. 15 March 2013. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
Dartmouth in Bloom has big plans to rescue one of the town's greatest assets, the community greenhouse, and restore it to its former Edwardian glory. The move comes at a time when the future of the community greenhouse is at risk, with controversial proposals from South Hams Council, which owns the building, to flatten it to extend the Mayor Avenue car park.
- ^ "Christopher Robin's Dartmouth bookshop to close". BBC News. 19 August 2011. Retrieved 25 October 2012.
- ^ . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 19 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 475.
- ^ . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 19 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 662.
- ^ . Dictionary of National Biography. Vol. 49. 1897. pp. 464–465.
External links
edit- Charles Oman, "Dartmouth and Kingswear Castles: Twin Dart estuary defenders"
- Dartmouth WebCam
- . The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 838.