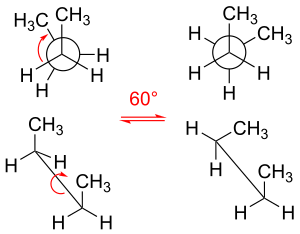
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted just by rotations about formally single bonds (refer to figure on single bond rotation). While any two arrangements of atoms in a molecule that differ by rotation about single bonds can be referred to as different conformations, conformations that correspond to local minima on the potential energy surface are specifically called conformational isomers or conformers.[1] Conformations that correspond to local maxima on the energy surface are the transition states between the local-minimum conformational isomers. Rotations about single bonds involve overcoming a rotational energy barrier to interconvert one conformer to another. If the energy barrier is low, there is free rotation[2] and a sample of the compound exists as a rapidly equilibrating mixture of multiple conformers; if the energy barrier is high enough then there is restricted rotation, a molecule may exist for a relatively long time period as a stable rotational isomer or rotamer (an isomer arising from hindered single-bond rotation). When the time scale for interconversion is long enough for isolation of individual rotamers (usually arbitrarily defined as a half-life of interconversion of 1000 seconds or longer), the isomers are termed atropisomers (see: atropisomerism).[1][3][4] The ring-flip of substituted cyclohexanes constitutes another common form of conformational isomerism.
Conformational isomers are thus distinct from the other classes of stereoisomers (i. e. configurational isomers) where interconversion necessarily involves breaking and reforming of chemical bonds.[5] For example, L/D- and R/S- configurations of organic molecules have different handedness and optical activities, and can only be interconverted by breaking one or more bonds connected to the chiral atom and reforming a similar bond in a different direction or spatial orientation. They also differ from geometric (cis/trans) isomers, another class of stereoisomers, which require the π-component of double bonds to break for interconversion. (Although the distinction is not always clear-cut, since certain bonds that are formally single bonds actually have double bond character that becomes apparent only when secondary resonance contributors are considered, like the C–N bonds of amides, for instance.) Due to rapid interconversion, conformers are usually not isolable at room temperature.
The study of the energetics between different conformations is referred to as conformational analysis.[6] It is useful for understanding the stability of different isomers, for example, by taking into account the spatial orientation and through-space interactions of substituents. In addition, conformational analysis can be used to predict and explain product selectivity, mechanisms, and rates of reactions.[7] Conformational analysis also plays an important role in rational, structure-based drug design.
Types
editRotating their carbon–carbon bonds, the molecules ethane and propane have three local energy minima. They are structurally and energetically equivalent, and are called the staggered conformers. For each molecule, the three substituents emanating from each carbon–carbon bond are staggered, with each H–C–C–H dihedral angle (and H–C–C–CH3 dihedral angle in the case of propane) equal to 60° (or approximately equal to 60° in the case of propane). The three eclipsed conformations, in which the dihedral angles are zero, are transition states (energy maxima) connecting two equivalent energy minima, the staggered conformers.
The butane molecule is the simplest molecule for which single bond rotations result in two types of nonequivalent structures, known as the anti- and gauche-conformers (see figure).
For example, butane has three conformers relating to its two methyl (CH3) groups: two gauche conformers, which have the methyls ±60° apart and are enantiomeric, and an anti conformer, where the four carbon centres are coplanar and the substituents are 180° apart (refer to free energy diagram of butane). The energy difference between gauche and anti is 0.9 kcal/mol associated with the strain energy of the gauche conformer. The anti conformer is, therefore, the most stable (≈ 0 kcal/mol). The three eclipsed conformations with dihedral angles of 0°, 120°, and 240° are transition states between conformers.[6] Note that the two eclipsed conformations have different energies: at 0° the two methyl groups are eclipsed, resulting in higher energy (≈ 5 kcal/mol) than at 120°, where the methyl groups are eclipsed with hydrogens (≈ 3.5 kcal/mol).[9]
While simple molecules can be described by these types of conformations, more complex molecules require the use of the Klyne–Prelog system to describe the different conformers.[6]
More specific examples of conformational isomerism are detailed elsewhere:
- Ring conformation
- Cyclohexane conformations, including with chair and boat conformations among others.
- Cycloalkane conformations, including medium rings and macrocycles
- Carbohydrate conformation, which includes cyclohexane conformations as well as other details.
- Allylic strain – energetics related to rotation about the single bond between an sp2 carbon and an sp3 carbon.
- Atropisomerism – due to restricted rotation about a bond.
- Folding, including the secondary and tertiary structure of biopolymers (nucleic acids and proteins).[10]
- Akamptisomerism – due to restricted inversion of a bond angle.
Free energy and equilibria of conformational isomers
editEquilibrium of conformers
editConformational isomers exist in a dynamic equilibrium, where the relative free energies of isomers determines the population of each isomer and the energy barrier of rotation determines the rate of interconversion between isomers:[11]
where K is the equilibrium constant, ΔG° is the difference in standard free energy between the two conformers in kcal/mol, R is the universal gas constant (1.987×10−3 kcal/mol K), and T is the system's temperature in kelvins. In units of kcal/mol at 298 K,
Thus, every 1.36 kcal/mol corresponds to a factor of about 10 in term of equilibrium constant at temperatures around room temperature. (The "1.36 rule" is useful in general for estimation of equilibrium constants at room temperature from free energy differences. At lower temperatures, a smaller energy difference is needed to obtain a given equilibrium constant.)
Three isotherms are given in the diagram depicting the equilibrium distribution of two conformers at different temperatures. At a free energy difference of 0 kcal/mol, this gives an equilibrium constant of 1, meaning that two conformers exist in a 1:1 ratio. The two have equal free energy; neither is more stable, so neither predominates compared to the other. A negative difference in free energy means that a conformer interconverts to a thermodynamically more stable conformation, thus the equilibrium constant will always be greater than 1. For example, the ΔG° for the transformation of butane from the gauche conformer to the anti conformer is −0.47 kcal/mol at 298 K.[12] This gives an equilibrium constant is about 2.2 in favor of the anti conformer, or a 31:69 mixture of gauche:anti conformers at equilibrium. Conversely, a positive difference in free energy means the conformer already is the more stable one, so the interconversion is an unfavorable equilibrium (K < 1). Even for highly unfavorable changes (large positive ΔG°), the equilibrium constant between two conformers can be increased by increasing the temperature, so that the amount of the less stable conformer present at equilibrium increases (although it always remains the minor conformer).
Population distribution of conformers
editThe fractional population distribution of different conformers follows a Boltzmann distribution:[13]
The left hand side is the proportion of conformer i in an equilibrating mixture of M conformers in thermodynamic equilibrium. On the right side, Ek (k = 1, 2, ..., M) is the energy of conformer k, R is the molar ideal gas constant (approximately equal to 8.314 J/(mol·K) or 1.987 cal/(mol·K)), and T is the absolute temperature. The denominator of the right side is the partition function.
Factors contributing to the free energy of conformers
editThe effects of electrostatic and steric interactions of the substituents as well as orbital interactions such as hyperconjugation are responsible for the relative stability of conformers and their transition states. The contributions of these factors vary depending on the nature of the substituents and may either contribute positively or negatively to the energy barrier. Computational studies of small molecules such as ethane suggest that electrostatic effects make the greatest contribution to the energy barrier; however, the barrier is traditionally attributed primarily to steric interactions.[14][15]
In the case of cyclic systems, the steric effect and contribution to the free energy can be approximated by A values, which measure the energy difference when a substituent on cyclohexane in the axial as compared to the equatorial position. In large (>14 atom) rings, there are many accessible low-energy conformations which correspond to the strain-free diamond lattice.[16]
Isolation or observation of conformational isomers
editThe short timescale of interconversion precludes the separation of conformational isomers in most cases. Atropisomers are conformational isomers which can be separated due to restricted rotation.[17] The equilibrium between conformational isomers can be observed using a variety of spectroscopic techniques.
Protein folding also generates stable conformational isomers which can be observed. The Karplus equation relates the dihedral angle of vicinal protons to their J-coupling constants as measured by NMR. The equation aids in the elucidation of protein folding as well as the conformations of other rigid aliphatic molecules.[18] Protein side chains exhibit rotamers, whose distribution is determined by their steric interaction with different conformations of the backbone.[19] This is evident from statistical analysis of the conformations of protein side chains in the Backbone-dependent rotamer library.
In cyclohexane derivatives, the two chair conformers interconvert with rapidly at room temperature, with cyclohexane itself undergoing the ring-flip at a rates of approximately 105 ring-flips/sec, with an overall energy barrier of 10 kcal/mol (42 kJ/mol), which precludes their separation at ambient temperatures.[20] However, at low temperatures below the coalescence point one can directly monitor the equilibrium by NMR spectroscopy and by dynamic, temperature dependent NMR spectroscopy the barrier interconversion.[21]
The dynamics of conformational (and other kinds of) isomerism can be monitored by NMR spectroscopy at varying temperatures. The technique applies to barriers of 8–14 kcal/mol, and species exhibiting such dynamics are often called "fluxional".
Besides NMR spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy is used to measure conformer ratios. For the axial and equatorial conformer of bromocyclohexane, νCBr differs by almost 50 cm−1.[20]
Conformation-dependent reactions
editReaction rates are highly dependent on the conformation of the reactants. In many cases the dominant product arises from the reaction of the less prevalent conformer, by virtue of the Curtin-Hammett principle. This is typical for situations where the conformational equilibration is much faster than reaction to form the product. The dependence of a reaction on the stereochemical orientation is therefore usually only visible in configurational isomers, in which a particular conformation is locked by substituents. Prediction of rates of many reactions involving the transition between sp2 and sp3 states, such as ketone reduction, alcohol oxidation or nucleophilic substitution is possible if all conformers and their relative stability ruled by their strain is taken into account.[22]
One example with configurational isomers is provided by elimination reactions, which involve the simultaneous removal of a proton and a leaving group from vicinal or antiperiplanar positions under the influence of a base.
The mechanism requires that the departing atoms or groups follow antiparallel trajectories. For open chain substrates this geometric prerequisite is met by at least one of the three staggered conformers. For some cyclic substrates such as cyclohexane, however, an antiparallel arrangement may not be attainable depending on the substituents which might set a conformational lock.[23] Adjacent substituents on a cyclohexane ring can achieve antiperiplanarity only when they occupy trans diaxial positions (that is, both are in axial position, one going up and one going down).
One consequence of this analysis is that trans-4-tert-butylcyclohexyl chloride cannot easily eliminate but instead undergoes substitution (see diagram below) because the most stable conformation has the bulky t-Bu group in the equatorial position, therefore the chloride group is not antiperiplanar with any vicinal hydrogen (it is gauche to all four). The thermodynamically unfavored conformation has the t-Bu group in the axial position, which is higher in energy by more than 5 kcal/mol (see A value).[24] As a result, the t-Bu group "locks" the ring in the conformation where it is in the equatorial position and substitution reaction is observed. On the other hand, cis-4-tert-butylcyclohexyl chloride undergoes elimination because antiperiplanarity of Cl and H can be achieved when the t-Bu group is in the favorable equatorial position.
The repulsion between an axial t-butyl group and hydrogen atoms in the 1,3-diaxial position is so strong that the cyclohexane ring will revert to a twisted boat conformation. The strain in cyclic structures is usually characterized by deviations from ideal bond angles (Baeyer strain), ideal torsional angles (Pitzer strain) or transannular (Prelog) interactions.
Alkane stereochemistry
editAlkane conformers arise from rotation around sp3 hybridised carbon–carbon sigma bonds. The smallest alkane with such a chemical bond, ethane, exists as an infinite number of conformations with respect to rotation around the C–C bond. Two of these are recognised as energy minimum (staggered conformation) and energy maximum (eclipsed conformation) forms. The existence of specific conformations is due to hindered rotation around sigma bonds, although a role for hyperconjugation is proposed by a competing theory.
The importance of energy minima and energy maxima is seen by extension of these concepts to more complex molecules for which stable conformations may be predicted as minimum-energy forms. The determination of stable conformations has also played a large role in the establishment of the concept of asymmetric induction and the ability to predict the stereochemistry of reactions controlled by steric effects.
In the example of staggered ethane in Newman projection, a hydrogen atom on one carbon atom has a 60° torsional angle or torsion angle[25] with respect to the nearest hydrogen atom on the other carbon so that steric hindrance is minimised. The staggered conformation is more stable by 12.5 kJ/mol than the eclipsed conformation, which is the energy maximum for ethane. In the eclipsed conformation the torsional angle is minimised.
In butane, the two staggered conformations are no longer equivalent and represent two distinct conformers:the anti-conformation (left-most, below) and the gauche conformation (right-most, below).
Both conformations are free of torsional strain, but, in the gauche conformation, the two methyl groups are in closer proximity than the sum of their van der Waals radii. The interaction between the two methyl groups is repulsive (van der Waals strain), and an energy barrier results.
A measure of the potential energy stored in butane conformers with greater steric hindrance than the 'anti'-conformer ground state is given by these values:[26]
- Gauche, conformer – 3.8 kJ/mol
- Eclipsed H and CH3 – 16 kJ/mol
- Eclipsed CH3 and CH3 – 19 kJ/mol.
The eclipsed methyl groups exert a greater steric strain because of their greater electron density compared to lone hydrogen atoms.
The textbook explanation for the existence of the energy maximum for an eclipsed conformation in ethane is steric hindrance, but, with a C-C bond length of 154 pm and a Van der Waals radius for hydrogen of 120 pm, the hydrogen atoms in ethane are never in each other's way. The question of whether steric hindrance is responsible for the eclipsed energy maximum is a topic of debate to this day. One alternative to the steric hindrance explanation is based on hyperconjugation as analyzed within the Natural Bond Orbital framework.[27][28][29] In the staggered conformation, one C-H sigma bonding orbital donates electron density to the antibonding orbital of the other C-H bond. The energetic stabilization of this effect is maximized when the two orbitals have maximal overlap, occurring in the staggered conformation. There is no overlap in the eclipsed conformation, leading to a disfavored energy maximum. On the other hand, an analysis within quantitative molecular orbital theory shows that 2-orbital-4-electron (steric) repulsions are dominant over hyperconjugation.[30] A valence bond theory study also emphasizes the importance of steric effects.[31]
Nomenclature
editNaming alkanes per standards listed in the IUPAC Gold Book is done according to the Klyne–Prelog system for specifying angles (called either torsional or dihedral angles) between substituents around a single bond:[25]
- a torsion angle between 0° and ±90° is called syn (s)
- a torsion angle between ±90° and 180° is called anti (a)
- a torsion angle between 30° and 150° or between −30° and −150° is called clinal (c)
- a torsion angle between 0° and ±30° or ±150° and 180° is called periplanar (p)
- a torsion angle between 0° and ±30° is called synperiplanar (sp), also called syn- or cis- conformation
- a torsion angle between 30° to 90° and −30° to −90° is called synclinal (sc), also called gauche or skew[32]
- a torsion angle between 90° and 150° or −90° and −150° is called anticlinal (ac)
- a torsion angle between ±150° and 180° is called antiperiplanar (ap), also called anti- or trans- conformation
Torsional strain or "Pitzer strain" refers to resistance to twisting about a bond.
Special cases
editIn n-pentane, the terminal methyl groups experience additional pentane interference.
Replacing hydrogen by fluorine in polytetrafluoroethylene changes the stereochemistry from the zigzag geometry to that of a helix due to electrostatic repulsion of the fluorine atoms in the 1,3 positions. Evidence for the helix structure in the crystalline state is derived from X-ray crystallography and from NMR spectroscopy and circular dichroism in solution.[33]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c Moss, GP (1996-01-01). "Basic terminology of stereochemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 1996)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 68 (12): 2193–2222. doi:10.1351/pac199668122193. ISSN 1365-3075. S2CID 98272391.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (1996) "Free rotation (hindered rotation, restricted rotation)". doi:10.1351/goldbook.F02520
- ^ Ōki, Michinori (1983) Recent Advances in Atropisomerism, in Topics in Stereochemistry, Vol. 14 (N. L. Allinger, E. L. Eliel and S. H. Wilen, Eds.), Hoboken, NJ:John Wiley & Sons, pp. 1-82; published online in 2007, DOI: 10.1002/9780470147238.ch1, see [1] and [2][permanent dead link], accessed 12 June 2014.
- ^ Alkorta, Ibon; Jose Elguero; Christian Roussel; Nicolas Vanthuyne; Patrick Piras (2012). Atropisomerism and Axial Chirality in Heteroaromatic Compounds. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry. Vol. 105. pp. 1–188. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-396530-1.00001-2. hdl:10261/62060. ISBN 9780123965301.
- ^ Hunt, Ian. "Stereochemistry". University of Calgary. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
- ^ a b c Anslyn, Eric; Dennis Dougherty (2006). Modern Physical Organic Chemistry. University Science. p. 95. ISBN 978-1891389313.
- ^ Barton, Derek (1970). "The Principles of Conformational Analysis". Nobel Media AB 2013. 169 (3945). Elsevier Publishing Co.: 539–44. Bibcode:1970Sci...169..539B. doi:10.1126/science.169.3945.539. PMID 17746022. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ^ J, McMurry (2012). Organic chemistry (8 ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. p. 98. ISBN 9780840054449.
- ^ Bauld, Nathan. "Butane Conformational Analysis". University of Texas. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
- ^ Dunbrack, R. (2002). "Rotamer Libraries in the 21st Century". Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 12 (4): 431–440. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(02)00344-5. PMID 12163064.
- ^ Bruzik, Karol. "Chapter 6: Conformation". University of Illinois at Chicago. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ^ The standard enthalpy change ΔH° from gauche to anti is –0.88 kcal/mol. However, because there are two possible gauche forms, there is a statistical factor that needs to be taken into account as an entropic term. Thus, ΔG° = ΔH° – TΔS° = ΔH° + RT ln 2 = –0.88 kcal/mol + 0.41 kcal/mol = –0.47 kcal/mol, at 298 K.
- ^ Rzepa, Henry. "Conformational Analysis". Imperial College London. Retrieved 11 November 2013.
- ^ Liu, Shubin (7 February 2013). "Origin and Nature of Bond Rotation Barriers: A Unified View". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 117 (5): 962–965. Bibcode:2013JPCA..117..962L. doi:10.1021/jp312521z. PMID 23327680.
- ^ Carey, Francis A. (2011). Organic chemistry (8th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 105. ISBN 978-0-07-340261-1.
- ^ Dragojlovic, Veljko (2015). "Conformational analysis of cycloalkanes" (PDF). Chemtexts. 1 (3). doi:10.1007/s40828-015-0014-0. S2CID 94348487.
- ^ McNaught (1997). "Atropisomers". IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications. doi:10.1351/goldbook.A00511. ISBN 978-0967855097.
- ^ Dalton, Louisa. "Karplus Equation". Chemical and Engineering News. American Chemical Society. Retrieved 2013-10-27.
- ^ Dunbrack, R. L.; Cohen, F. E. (1997). "Bayesian statistical analysis of protein side-chain rotamer preferences". Protein Science. 6 (8): 1661–1681. doi:10.1002/pro.5560060807. ISSN 0961-8368. PMC 2143774. PMID 9260279.
- ^ a b Eliel, E. L.; Wilen, S. H.; Mander, L. N. (1994). Stereochemistry Of Organic Compounds. J. Wiley and Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-01670-0.
- ^ Jensen, Frederick R.; Bushweller, C. Hackett (1969-06-01). "Separation of conformers. II. Axial and equatorial isomers of chlorocyclohexane and trideuteriomethoxycyclohexane". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 91 (12): 3223–3225. doi:10.1021/ja01040a022. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ^ Schneider, H.-J.; Schmidt, G.; Thomas F. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1983, 105, 3556. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja00349a031
- ^ Rzepa, Henry S. (2014). "Cycloalkanes". Imperial College London.
- ^ Dougherty, Eric V. Anslyn; Dennis, A. (2006). Modern Physical Organic Chemistry (Dodr. ed.). Sausalito, CA: University Science Books. p. 104. ISBN 978-1-891389-31-3.
- ^ a b IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "torsion angle". doi:10.1351/goldbook.T06406
- ^ McMurry, J.E. (2003). Organic Chemistry (6 ed.). Brooks Cole. ISBN 978-0534000134.
- ^ Pophristic, Vojislava; Goodman, Lionel (2001). "Hyperconjugation not steric repulsion leads to the staggered structure of ethane". Nature. 411 (6837): 565–568. doi:10.1038/35079036. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 11385566.
- ^ Weinhold, Frank (2001). "A new twist on molecular shape". Nature. 411 (6837). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 539–541. doi:10.1038/35079225. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 11385553.
- ^ Weinhold, Frank (2003-09-15). "Rebuttal to the Bickelhaupt–Baerends Case for Steric Repulsion Causing the Staggered Conformation of Ethane". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 42 (35): 4188–4194. doi:10.1002/anie.200351777. ISSN 1433-7851.
- ^ Bickelhaupt, F. Matthias; Baerends, Evert Jan (2003-09-15). "The Case for Steric Repulsion Causing the Staggered Conformation of Ethane". Angewandte Chemie (in German). 115 (35): 4315–4320. Bibcode:2003AngCh.115.4315B. doi:10.1002/ange.200350947. ISSN 0044-8249.
- ^ Mo, Yirong; Wu, Wei; Song, Lingchun; Lin, Menghai; Zhang, Qianer; Gao, Jiali (2004-03-30). "The Magnitude of Hyperconjugation in Ethane: A Perspective from Ab Initio Valence Bond Theory". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 43 (15). Wiley: 1986–1990. doi:10.1002/anie.200352931. ISSN 1433-7851. PMID 15065281.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "gauche". doi:10.1351/goldbook.G02593
- ^ Conformational Analysis of Chiral Helical Perfluoroalkyl Chains by VCD Kenji Monde, Nobuaki Miura, Mai Hashimoto, Tohru Taniguchi, and Tamotsu Inabe J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 2006; 128(18) pp 6000–6001; Graphical abstract