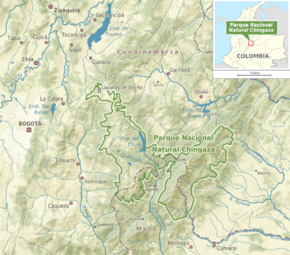
Chingaza National Natural Park (Spanish: Parque Nacional Natural (PNN) Chingaza) is located in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, northeast of Bogotá, Colombia in the departments of Cundinamarca and Meta. The elevation in the park, to the east of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, ranges from 800 to 4,020 metres (2,600 to 13,200 ft), and the temperature ranges from 4 to 21.5 °C (39 to 71 °F).[2] The park extends over the Cundinamarca municipalities La Calera, Fómeque, Guasca and San Juanito (Meta).
| Chingaza National Natural Park | |
|---|---|
 Road in Chingaza National Park | |
| Location | Colombia |
| Coordinates | 4°33′N 73°42′W / 4.550°N 73.700°W |
| Area | 766 km2 (296 sq mi) |
| Established | 1977 |
| Governing body | SINAP |
| Official name | Sistema Lacustre de Chingaza |
| Designated | 25 June 2008 |
| Reference no. | 1782[1] |
Etymology
editThe name Chingaza comes from Chibcha and means "middle of the width".[3]
Hydrography
edit99% of the park area is located in the Orinoco River basin in the upper basins of the Black and White, Guatiquía, Guacavía, Gazaunta, Gazamumo, Humea and Guavio rivers. 1% of its area is in the Magdalena River basin, where the San Lorenzo Creek, La Calera River tributary, and Teusacá, Siecha, Bogotá, and Tominé rivers drain.
Chingaza has about 40 natural glacial lakes. The largest lake is Lake Chingaza, located in the southwestern part of the park at an altitude of 3,250 metres (10,660 ft). One of the most representative and culturally significant bodies of water are the Siecha Lakes, a group of three lakes in the municipality of Guasca. Chuza Reservoir is also located within the Chingaza Park in the basin of a tributary of the River Chuza Guatiquía. This reservoir is the center of the Bogotá Water Company's Chingaza System. Chingaza contributes 80% of the city's high quality drinking water.[4]
Viewing and wildlife
editThe animals found in Chingaza include the spectacled bear, deer, tapirs, pumas, Andean condors, cock-of-the-rocks, jaguars, turkeys, woolly monkeys, nocturnal monkeys, ocelots, and toucans. The large number of endemic species makes the Eastern Ranges one of the most important geographic regions for wildlife in Colombia.[2]
In the vicinity of the Chingaza lake, less than 383 species of plants have been recorded. It is estimated that the total flora of the park may exceed 2,000 species. There are eight species of peat moss, which can absorb up to 40 times their weight in water. There are also endemic species, such as frailejones, that grow on the páramo and even within forests.[4]
Communities present in the area
editIndigenous
editThere are currently no indigenous groups within the territory of Chingaza. However, the area has historical importance, with over 10,000 years of Muisca and pre-Muisca inhabitation in the region. Ponds, rock shelters, the mountains and especially the Siecha Lakes were sacred places of worship and respect, forming ceremonial centers.[5] Recent studies indicate that Chingaza in the Chibcha language of the Muisca could have been called Chim-wa-za, which means "God's Night Mountains".[6]
Smallholder farmers
editThe population around the park forms a rural community with its own forms of organization, dynamic internal and external relationships, and cultural patterns that distinguish it from smallholder farmer communities in other regions.[6]
Named after Chingaza
edit- Araneus chingaza, a species of spider described in the Chingaza Natural National Park
- Ischnura chingaza, a species of dragonfly, idem
- Polylobus chingaza, a species of beetle, idem
- Epidendrum chingazaënse, a species of orchid.
Gallery
edit-
Clouds over Chingaza National Park
-
Siecha Lakes
-
Lake in the southern part of the park
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Sistema Lacustre de Chingaza". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ^ a b (in Spanish) Website Chingaza Natural National Park Archived 2017-10-15 at the Wayback Machine - accessed 06-05-2016
- ^ (in Spanish) Etymology Chingaza[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b (in Spanish) Chingaza Natural National Park Archived 2016-08-06 at the Wayback Machine - GuiaTodo - accessed 06-05-2016
- ^ Ocampo López, Javier (2007). Grandes culturas indígenas de América [Great indigenous cultures of the Americas] (in Spanish). Bogotá, Colombia: Plaza & Janes Editores Colombia S.A. p. 226. ISBN 978-958-14-0368-4.
- ^ a b (in Spanish) PNN Chingaza Archived 1 March 2019 at the Wayback Machine