The bushy-tailed mongoose (Bdeogale crassicauda) is a mammal in the family Herpestidae found in central Africa, from southern Kenya to central Mozambique.
| Bushy-tailed mongoose | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Herpestidae |
| Genus: | Bdeogale |
| Species: | B. crassicauda
|
| Binomial name | |
| Bdeogale crassicauda Peters, 1852
| |
| |
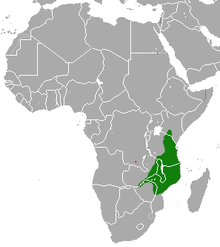
| Bushy-tailed mongoose range (green - extant, pink - probably extant) | |
Characteristics
editThe bushy-tailed mongoose has a greyish to yellowish brown fur. The underfur is dense, and the guard hairs are 5–45 mm (0.20–1.77 in) long. Its head is rounded.[2] It has short woolly ears and a plush muzzle. Its tail is wide and bushy.[3] Five individuals captured in Arusha National Park had a head-to-body length of 383–407 mm (15.1–16.0 in) with a 230 mm (9.1 in) long tail and a 74.9–77.7 mm (2.95–3.06 in) long feet; they weighed 1.273–1.3 kg (2.81–2.87 lb).[4]
Taxonomy
edit- B. c. crassicauda, central Mozambique, Malawi and Zambia
- B. c. nigrescens, Central Kenya (Nairobi)
- B. c. omnivora, found in northern coastal Tanzania and Kenya
- B. c. puisa, northern Mozambique and southern Tanzania
- B. c. tenuis
Phylogeny
editThe bushy tailed mongoose is closely related to the black-footed mongoose (Bdeogale nigripes). Perez's study of genes within the family Herpestidae showed the genus Bdeogale is monophyletic. Close cousins of this clade include the genera Ichneumia and Cynictis.[3]
Distribution and habitat
editBecause of the bushy-tailed mongoose's size and stealthiness, its range is not completely known. Although, it apparently prefers locations near rivers that provide cover.[2] The bushy-tailed mongoose inhabits foremost open shrubland and multilayered forest. These habitats vary little in temperature and humidity.[4] In northern Tanzania, the bushy-tailed mongoose was recorded in more than 31 camera trap locations in Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Biharamulo-Burigi-Kimisi Game Reserve and Mahale Mountains National Park, mostly in Acacia woodlands and riparian zones.[5]
Conservation
editThe bushy-tailed mongoose is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. It is negatively impacted by habitat degradation and fragmentation, prey depletion and land use dynamics caused by cattle grazing.[1]
References
edit- ^ a b White, P.A.; Fischer, C.; Hausser, Y.; Foley, C.; Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Bdeogale crassicauda". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41591A97163568. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41591A97163568.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ a b Taylor, M.E. (1987). "Bdeogale crassicauda". Mammalian Species (294): 1–4. doi:10.2307/3503826. JSTOR 3503826.
- ^ a b Perez, M.; Li, B.; Tiller, A.; Cruaud, A. & Veron, G. (2006). "Systematic Relationships of the Bushy-tailed and Black-footed Mongooses (genus Bdeogale, Herpestidae, Carnivora) Based on Molecular, Chromosomal and Morphological Evidence". Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research. 44 (3): 251–259. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0469.2006.00359.x.
- ^ a b Martinoli, A.; Preatoni, D.; Galanti, V.; Codipietro, P.; Kilewo, M.; Fernandes, C.A.R.; Wauters, L.A. & Tosi, G. (2006). "Species Richness and Habitat Use of Small Carnivores in the Arusha National Park (Tanzania)". Biodiversity & Conservation. 15 (5): 1729–1744. doi:10.1007/s10531-004-5020-2. S2CID 24864567.
- ^ Pettorelli (2010). "Carnivore biodiversity in Tanzania: Revealing the distribution patterns of secretive mammals using camera traps". Animal Conservation. 2. 13 (2): 131–139. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1795.2009.00309.x. S2CID 84216019.
External links
edit- Bushy-tailed mongoose, Tanzanian Mammal Atlas Project
