Bondage in BDSM is the activity of tying or restraining people using equipment such as chains, cuffs, or collars for mutual erotic pleasure.[1] According to the Kinsey Institute, 12% of females and 22% of males respond erotically to BDSM.[1]

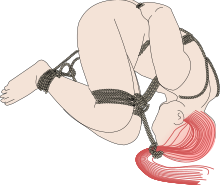
A number of bondage positions and methods are used in rope bondage and other BDSM activities. Ropes are a common element of these positions, although straps, webbing, chains, hooks, manacles, spreader bars, collars, common furniture, purpose-built frames, various gags and monogloves may also be used. The ties and frictions often are variants of Japanese bondage, shibari and kinbaku from where they derived.
Whole body ties
editBall tie
editThe ball tie is a bondage position in which a person is bound into a ball position with the knees against the shoulders.[2] A ball position (also called a fetal position) can be tightly bound so that the legs are also bent double so the heels press against the buttocks; the legs must be brought up so that the thighs are pressed against the chest. Pressing the thighs tightly against the abdomen may restrict breathing.
The hands may be tied either in front or behind the back, however behind the back is more typical. If behind, there may also be elbow bondage,[3] or the arms may be in a reverse prayer position, with ropes round the arms and torso (or arms and legs) to hold the arms firmly against the back. If in front, the arms may be tied hugging the legs, or possibly with each wrist bound to the opposite elbow. The ankles may also be tied together, as well as the knees. Typically, the ankles are tied to the thighs in a frogtie.[citation needed]
Sometimes the submissive wears high-heeled shoes and has ropes wrapped round the heels and fixed to the wrists. This adds to the visual impact, and should be used as a supplement to other secure bondage. Under strain, the shoes may come off or the heels may break off. When tied this way, the shoes cannot be removed.[citation needed]
The head may be pulled back in some way, such as in head bondage. However, purists argue that this goes against the idea of binding into a ball. Alternatively, the head can be pulled forward to force the chin to press against the chest.[citation needed]
The position can be stringent while stimulating. At the same time, it is comfortable and the subject may remain in it for quite some time.[4]
The ball tie is one of the positions possible in self-bondage. The mobility is limited so extra independent escape mechanisms should be used over and above the usual bondage precautions.[citation needed]
Hogtie bondage
editHogtie bondage requires all four limbs to be tied together behind the back. It typically involves connecting a person's wrists and ankles behind the back using some form of physical restraints such as rope or cuffs, but may in some BDSM contexts also refer to the binding of arms and legs behind the back.[2] The binding may be loose with the ankles and wrists some distance apart, or more stringent with all four bound together even with the wrists and ankles crossing and being cinched to the knee or shoulder harness.[2]
A classic western hogtie would be made more stringent by binding together the elbows and binding together the knees.[2]
A variation of the hogtie involves tying bound wrists to frogtied legs, providing the dominant easier access to the submissive's crotch for sexual play.
Safety
editThe hogtie position places pressure on the abdomen of the tied person, which may create difficulty in breathing known as postural asphyxia.[5] Care should be taken to ensure the person being bound can breathe easily throughout all stages of play.[6] This is particularly important if gags, collars or rope are used to create a more stringent tie.
Crab tie
editThe submissive's wrists are tied to the ankles, and the elbows attached to the knees. It is restrictive, allowing only the opening and closing of the legs and some rolling.[2]
Shrimp tie (ebi)
editA shrimp tie (海老責め, ebi-zeme) (also known as an ebi (海老) or a kuri (繰り)) is a type of Kinbaku bondage. A chest tie, such as a box tie, is constructed. The participant sits cross-legged, and the ankles are tied together using a single column tie. The rope is looped over the participants neck (or chest harness), and back to the ankles; this is then progressively tightened, bringing the ankles up to the head.[7][8][9]
Due to the forced bent-down position of the upper body, this position sends a burning sensation through the body if the subject remains in it for a long time.[10][11] As the knees are widely spread, the position resembles the legs of a prawn or shrimp.
The shrimp tie originated over 300 years ago in 1742 in Japan as a torture and interrogation technique.
Variations
edit- Knees are bound inward to further restrict movement
- The ankles are tied to the neck instead of the chest harness
All variations have the crossed position of the ankles in common.
Reverse shrimp tie
editA Gyaku ebi: A chest tie, such as a box tie, is constructed. The participant sits cross-legged, and the ankles are tied together using a single column tie. The participant is moved onto their stomach, and the rope is passed from ankles along the back, pulling them and securing them to the buttocks. This is also called the Japanese hog-tie.[12][13]
Rope harness
editA bondage rope harness (sometimes referred to as a bondage web, rope web, rope dress, or karada) is a binding which involves the tying of an intricate structure of rope around the body in a complex web-like fashion.
A rope harness is similar in effect to a leather bondage harness, in that both are not in themselves normally used to bind a person, but are used to apply pressure over the area bound and can provide securing points for other bondage techniques, including suspension bondage.[14]
A rope harness uses around 10–15 m of rope to tie, and involves multiple passes of rope from front to back around the body to build up the characteristic diamond-shaped rope pattern. It typically starts from a rope halter, the double rope with four specifically placed overhand knots falls down the body, and is pulled loosely beneath the crotch and up to the back of the neck halter. The single strands are then passed from back to front, looping into the stem or using Munter hitches. In some cases, a rope harness may extend beyond the torso, into diamond-patterned webs that extend down the length of the arms or legs.[14]
Though a rope harness is not normally used to bind the limbs, it can be used for that purpose by simply going around the arms rather than under. A rope harness can be used with a crotch rope or a shinju ("pearl") breast harness.
Japanese karada
editThe Japanese term shibari means simply "a tie", while kinbaku is a decorative tie; where the aim is to produce a beautiful rope pattern around the body.[15] The Japanese term karada means simply "body". Traditionally, a distinction was made between kikkou ("turtle-shell" pattern; hexagonal) and hishi (diamond) patterned ties, although many modern sources just use the term kikkou to refer to any rope body harness.[12]
Ties of the lower body
editCrotch rope
editA crotch rope (known in Japanese bondage as Matanawa, Sakura [16] or Sukaranbo [17]) is a rope that passes between the labia to apply painful or pleasurable pressure to the vulva. The rope is anchored by being tied around the waist. A crotch rope is most commonly made of hemp or jute, but webbing, straps or a harness are also used. It is sometimes combined with other bondage techniques including predicament bondage.[18]
A crotch rope may be tied over clothing or directly onto the skin; it can be worn under clothing or in full view. While crotch ropes are most commonly used on women, variations exist for use on men.[19] A crotch rope can also be used as an unsophisticated type of chastity belt.[20]
Technique
editA crotch rope may consist of either a single line running between the legs to stimulate the genitals, or two lines running either side of them to leave them exposed.[19] In the former case, the rope may pass between the labia majora[21] or deeper through the pudendal cleft of the vulva. Knots can be tied in the rope to apply specific pressure to the anus or clitoris.[17] A crotch rope is usually fixed in place by tying it to a rope around the waist just above the hips or by tying the two ends to a fixture. Crotch ropes are sometimes used in BDSM activities, especially on female submissives, most commonly as a part of tease and denial. A crotch rope is sometimes combined with the damsel in distress pose used in silent films, where the arms are tied together behind the back at the elbows and wrists, and the legs are tied together at the knees and ankles.[2]
Variations
editFor abrasion play if the rope is not tied to the waist it can be moved forward and backward between the labia or the subject can be made to walk across it.
The ropes may be wrapped tightly around the waist and tied off in front, fed down across the genitals, then pulled back up behind and tied to other cords wrapped around the wrists, doubling as a cinch to tighten them further. This allows the rope bound person some ability to vary pressure on the genitals (often causing sexual stimulation) at the cost of reduced freedom of movement. If such a cord is pulled extremely tight the wrists and arms will have very little freedom of movement particularly when combined with elbow bondage and the hands will be firmly forced in contact with the buttocks.[22]
Frogtie
editThe frogtie is a lower-body bondage position in which a person's legs are bent fully at the knees. They are bound separately ankle-to-thigh, and also just behind the knee, in the likeness of a crouched frog.[2] The knees may be left free, closely together or widely spread. This is the starting point of many other ties.
This tie places the person in a position where they are vulnerable but not completely immobilized and can still move about, albeit in an awkward crawling motion. The frogtie, with the person restrained so, can also be used as a restrictive sex position or as a basis for more restrictive bondage. The bound person's wrist tie can also be tethered to some sort of immovable ring by an arbitrary length of cord, allowing some limited freedom of movement while preventing escape. Kinbaku enthusiasts could use a futumomo tie.[20]
The wrists on each side are often then tied to the ankle/thigh combination on their respective sides, although it is possible to tie each wrist to the opposite ankle and make the position noticeably more strict.[15]
In a similar position, the person's wrists are simply bound to their corresponding ankles. However, that position cannot be fully considered as a frogtie, because it does not match the "bound ankle-to-thigh" condition.
Positions of the legs
editThe legs may be tied together, sometimes described as the "virgin position", or apart, known as the "slut position".[15] The submissive can be standing, kneeling, sitting, or have the knees drawn up to the chest. The standing position may be relaxed, on tiptoe, or, at the most extreme, en pointe.[15] A common technique in Japanese bondage is for the bound person to stand on one leg while the ankle of the other leg is bound to the standing thigh. This is a form of asymmetric bondage and the lack of balance is disorientating for the subject.[23]
Lotus position
editSome more flexible submissives are comfortable sitting in the yoga lotus position.[2]
Ties of the upper body
edit
Box tie
editThe box tie is a tie of the chest and upper arms, and is combined to create with ties of the lower limbs as a component or variation of other ties. Both arms are supported in parallel behind the back by a core and made immobile by a tensioned rope connecting the midpoint of the upper arms.[2]
The TK wrap or shibari box tie, gote shibari, is a single column tie of the upper body. It is also called a takate kote.[24] The forearms are placed in parallel high behind the back. This forms the starting point for the tie that has a top rope that encircles the torso and arms just below the shoulder, tying back to a central point, creating a stem down to the forearms. This is the distinguishing feature of the box-tie. A lower rope encircles the arms and torso at a midpoint between the upper rope and elbow, tying back to the stem.[25]
TK wraps are used in suspension bondage, and if the ropes are misplaced the body weight can crush the radial nerve leading to the serious and possibly irreversible condition known as wrist drop. There is no absolutely safe position for the top wrap; the mid-point gap between the triceps and the deltoid muscles is the most problematic.[24]
Variants
editThe cross-chest boxtie replaces the top rope by one that passes over the shoulder and back under the opposite arm, reverses tension and then repeats over the other shoulder.[26]
A more strenuous alternative is the elbows together tie, which can lead to a strappado, or the reverse-prayer ties The over-arm (Hasenohren) or bunny ears ties, method is another way of restraining the hands.[2]
The Star Harness restrains the arms.[27] There is also the Pentagram (Star Harness).[28]
Breast bondage
editBreast bondage is a bondage technique which involves the tying of rope around a woman's breasts in a visually intricate and decorative pattern. Breast bondage most commonly uses rope, but webbing, straps, a bondage harness[29] or bondage tape may also be used.[30]
Breast bondage often focuses on the decorative, aesthetic and erotic aspects of the result, and not on immobilization of the female subject. However, breast bondage can be combined with other techniques which restrict the subject's mobility and can provide securing points for other bondage plays, such as crotch rope and breast torture.[31][32] Hence it can be used as an expression of dominance and submission as well as an aesthetic kink.[33]
Technique
editBreast bondage can be applied over clothing or directly to the skin, and can be worn under clothing or in full view. 1⁄4 inch (0.6 cm) rope, ribbon, or leather straps can be used.[34]
The basic breast bondage technique, sometimes known as circling,[30] involves tying ropes around the base of the breasts, causing them to bulge outwards. Usually, a single length of rope is used to tie both breasts so that the rope harness is automatically held together at the front. The rope may then also be fixed behind the back, to make a sort of bra.[34] The technique is most suitable for breasts that are C cup or larger.[30]
Another technique is to put a rope around the torso just above the breasts, and another one just below them, then push the ropes together to squeeze the breasts from the top and bottom. This can be done instead of, or as well as, the other method. A rope can also be passed over the shoulders and between the breasts, drawing the rope above and below the breasts together, then pass back over the shoulders to the knots at the back. The primary rope can be used to place cinches between the arms and the body.[34]
Shinju
editShinju is a traditional Japanese breast bondage technique in which a rope is tied above, below and between the breasts, and also forms a halter over the shoulders and around the neck.[30] The term Shinju (from the Japanese 真珠 meaning pearl) is a euphemism to refer to the binding of female breasts. It has been popularly claimed that "shinju" is an authentic Japanese term for a "bikini harness". However, no such tie called a "shinju" is found in historic or present kinbaku.[31]
The basic or foundational kinbaku form of binding the arms and breasts is known as the Ushiro Takatekote, which is to bind the arms behind (ushiro) the back in a box arm position (takate kote). This basic box arm tie, originally found in the samurai martial art of hojōjutsu (捕縄術) or Nawajutsu, (縄術) evolved into its erotic usage at the end of the 19th century and early 20th century, and is the foundation of most other kinbaku ties.[35]
Combination with other techniques
editSometimes, breast bondage is combined with other bondage techniques. For example, the woman's arms can be tied behind her back, in an elbow or box tie or in a reverse prayer position. When combined with breast bondage, bound arms force the woman's chest and breasts to protrude further. When combining breast and arm bondage, the ropes can draw the ropes above and below the breasts together at the sides of the breasts as they pass under the shoulders and behind the neck, thus resulting in rope effectively surrounding the breasts.[citation needed]
Breast bondage can play an integral part in suspension bondage. If the subject is being suspended, particularly in a horizontal position such as a suspended hogtie, breast bondage is used as the main supporting area under the chest.[citation needed]
Positions of the arms
editTo describe a rig, a whole vocabulary has evolved. When the arms are crossed over the chest like a mummy: this is Egyptian, if they touch the opposite shoulders: this is a double-V.[2] When both wrists are secured together behind the waist: this is a strappado. When a wrist is pulled behind the back and up to the opposing shoulder we have a hammerlock.[2] When the wrists are in front of the body and the elbows tied with a spreader bar behind: this is a waitress. This hands may be on the head, or behind the neck or in an over-arm tie. They may be on the soles of the feet, on the ankles,[36] on the opposite ankles on the knees, to the side crossed in front or holding the opposite elbow.[15]
Captive tie
editA captive tie or over-arm tie (Kotobu Ryo-tekubi), is a bondage position in which a person's wrists are fastened behind the person's head using some form of physical restraints, such as rope or cuffs to which is attached a length of rope, chain or strap the other end of which is attached to a belt at the waist or other anchoring point.[37]
People who practice rope bondage see this as a short term or temporary tie, to be used to restrain the submissive while moving to another room, or a warm up introductory tie. It is not inescapeable.[38] This simple over-arm tie is sometimes used in sexual foreplay and in tickling games where it prevents the submissive from protecting their ticklish spots.
The wrists are tied together in front with a double column tie. They are taken over the head and the rope falls down the centre of the back. It is passed around the lower chest and looped around itself, it is reversed and the fall is tightened and centred, the rope passes back in front of the chest and is locked off at the centre back. Spare rope can be passed up to wrists tightening the tie. To use this as a permanent tie, the tension is reduced and a further rope is passed between the upperarms, closing the space under the elbows.[38] The over-arm tie may be used as a part of more complicated bondage. For example, the back rope can be passed between the legs and fastened in front, forming a crotch rope. The wrists may be tied to the upper arms with any desired tension, from a loose tie to a strict tie where the wrists are almost touching the upper arms.[37] The over-arm tie can be combined with other techniques which restrict the subject's mobility further, such as hogtie bondage, frogtie or the shrimp tie for the legs, or by securing the tied wrists to a fixed frame. In this position, the elbows stick out on each side, level with the head, with the hands tied behind the head.[citation needed]
Shouldering the rifle
editTeppō shibari (Japanese: 鉄砲縛り)
This is an asymmetric arm tie, where one arm is taken behind the back, and the other arm is taken over the shoulder.[39][15]
Reverse prayer
editThe reverse prayer position, a technique used in BDSM play, involves restraint of a person's arms by binding them behind the person's back, with the hands placed between the shoulders, with the fingers of both hands straight, extended, and the palms of the hands touching each other.[15] The wrists are bound together. It is similar to the traditional prayer position, but with the arms behind, rather than in front of, the bound person, thus preventing use of the arms. Someone bound in the position may need careful monitoring. Many people find the position painful after a time, and cramps may set in.
To immobilize the arms further, ropes or a strap are often placed round the arms and torso, pressing the arms against the back. On a woman, this can conveniently be linked to ropes for breast bondage. Another technique is to fix ropes from the elbows to a belt or other ropes round the body.
In bondage fiction, people in this position are sometimes forced to have their elbows touching, turning this into a form of elbow bondage. Very few people can adopt this position without dislocation of the shoulders. However, with many people, it is possible to press the elbows together slightly and tie them in that position.
The reverse prayer position (without any bondage) is also used in some yoga exercises.[40]
Head bondage
editHead bondage, in BDSM play, includes all techniques used to apply control to the head of the subject. It may refer to one of several techniques:[41]
- It may refer to the use of rope or other material to achieve control of the head. In particular, it may refer to pulling the head backwards by hair bondage or a rope attached to the back or top of a hood or head harness. It is also possible to use a rope attached to a blindfold or gag, but this is usually less secure and may cause excessive pressure on a small part of the face; in particular, with a gag, the corners of the mouth may be injured.
- It may refer to encasing the head in a bondage hood, a head harness (a device made of interconnected straps designed to encircle the human head), a box, or the use of a device such as a Scold's bridle (also referred to as a branks). A head harness may include a blindfold and/or gag. The encasement may include or be supplemented by a wide, stiff posture collar round the neck to restrict movement of the head.[41]
The straps of a head harness are generally secured by buckles that fasten at the back of the head. Head harnesses are most commonly used to provide points of attachments to secure various kinds of gags, such as ball gags, bit gags, muzzle gags and ring gags, although they also have other uses, such as providing attachment points for other forms of bondage, or may be used simply for their psychological effect. Head harnesses may also function as a gag by themselves, by restricting the ability to open the mouth, or have a mouth cover as an integral part.[42]
Head harnesses, like many other forms of bondage, also have the effect of creating a sense of objectification and erotic helplessness in the wearer, which can be erotic for the wearer, or for those observing them. Many head harnesses are designed with straps that pass in front of the wearer's eyes, restricting their vision, and further increasing the sense of objectification and erotic subjugation. Some have full blindfolds.[41]
Ties to anchor points
editSpread eagle
editThe spread eagle position is also employed as a bondage position in BDSM play, sometimes horizontally otherwise vertically and even upside down. This is a comfortable position, the submissive lies face up on their back with all four limbs secured to the furniture. Face down would be called prone. The ties can be slack allowing movement or more severe. The position allows for total front access, but none to the rear, so it excludes spanking games. Penetration is limited by the low angle.[43]
X-cross
editA standing or hanging spread eagle position can be achieved using equipment such as an X-cross (also referred to as Saint Andrew's cross) or spreader bars or with ropes or chains attached to different endpoints.[44] As an erotic humiliation technique, it forces the subjects to display their genitals and to provide access to the crotch, groin or anal region.[citation needed]
Bondage furniture
editSpecialist bondage furniture with anchor points is manufactured. It encompasses cages, frames, stocks, chairs and tables.[45] Standard household furniture can be discretely adapted. For instance, a bed can be adapted using a restraints kit; webbing attached to leather cuffs is placed under the mattress. A ladder back chair offers anchor points for binding the legs high in the air, or behind.[46]
Strappado
editStrappado bondage is a term describing a position and technique used in BDSM play. A person's arms are bound behind their back, then by use of some method of attachment such as a rope or chain that runs from their wrists to a securing point above, their arms are lifted behind them until the person is forced to bend forward.[47][2] While the strappado bondage position is considered to be a form of BDSM play, it shares its basic principles of restraint with the method of torture and therefore can very easily become just that if not practiced safely.[48][2]
Techniques
editThe different styles of the strappado bind can be summarized as follows and these can be combined with crotch ropes and breast bondage, gags or blindfolds. The exact technique used is very much related to the purpose of using this particular position in BDSM play:
- legs apart – spreader bar or attachment points[49]
- legs together
- knees bound together and ankles spread apart
- elbows bound / not bound (see also armbinder)
- rope around neck/collar pulling down to force increased bend (in the interests of safety, it is important to ensure that there is no pressure on the front of the neck)
- hair bondage or other head bondage to pull head back[49]
It intentionally reduces the subject's ability to struggle, as the body is placed in an awkward position such and any struggling on their part, could result in their losing balance. As a result, the subject chooses not to move for fear of falling over. It creates a sense of vulnerability in the subject's mind by exposing their buttocks and genital area. When the elbows are bound together, even for very flexible subject it is rarely possible to bind them to touch, for as arms are lifted towards a horizontal position, the shoulder joints shift into a different position preventing the usual movement that should occur when the elbows are drawn together. Irrespective of this any elbow bondage, even minor, applied in this manner may severely increase tension and pain.[49]
The use of head bondage allows the subject's head to be pulled back to a front-facing position as opposed to hanging towards the floor and is often used to make the subject perform oral sex. In addition to the restrictiveness that this causes, if a suitable ring gag is used the subject may feel increasingly exposed to penetration and because the subject's head is facing down drooling may also occur.[49]
The normal reaction of the subject is to increase the forward bending as the arms are lifted. By further lifting the arms beyond a critical point this may become too difficult or even physically impossible to continue without lifting themselves off the floor and force them to stand more upright and increase the strain on the shoulder joints. The subject can also be secured to e.g. a frame and ropes or chains substituted for other bondage devices. By completely immobilizing the subject's body the person in the dominant position can have complete and precise control over the tension and pain experienced.[49]
A form of predicament bondage is to tie one foot of the subject to the opposite thigh or another body part so they have to concentrate on not causing more pain. Their arms are raised to the point where they have to stand on their toes. To relieve pain in their foot they must lower their body and cause more pain in their shoulders. To relieve pain in their shoulders they must stand on tip-toes and cause more pain in their foot and leg. Another variation is to tie the subject's foot to a body part of another subject so they can relieve their own pain but increase it for the other subject.[49]
With the breasts pointing towards the floor, the use of nipple clamps, possibly with weights attached, can be used to stimulate the subject with more pain.
Strappado bondage is most commonly used with the subject's feet on the ground. Very rarely will someone use this technique with their feet off the ground, because of the pain and possibly severe injury this can cause.[49]
Due to the difficulty of maintaining this position, this type of BDSM play does not allow for long periods of being bound. Its major use is for sexual play with the bound subject. While bound like this, the subject is open to the use of various tools such as floggers, whips, etc., as well as general spanking. This position can also be used for sexual intercourse, or the use of vibrators and/or dildos to stimulate the bound person.[49]
Precautions and safety
editThis bondage position is also used as a form of torture, therefore measures are usually taken to ensure that the subject bound in this position is not pushed beyond their physical capabilities. Any position that moves limbs into an extreme position and holds them there for an extended period of time can result in damage—sometimes permanent—to even the most flexible of people. It is possible, though very rare, for extreme iterations of this position to cause asphyxiation, as being suspended in this way can constrict the lungs and cause respiratory distress. Therefore, it is a technique to be performed with safety foremost in mind.[49][6]
Suspension
editSuspension bondage is a form of sexual bondage where a bound person is hung from one or more overhead suspension points. Suspension bondage is considered to carry a higher risk than other forms of sexual bondage and there is much attention to safety.[50]
In partial suspension the person is bound in a way that part of their body weight is held by suspension ropes, cables or chains. The classic partial suspension position is to have the person balancing on one foot with part of their weight supported through a chest harness and the other leg pulled up in some direction. A person lying on their upper back with legs tied upwards to a suspension point to pull their lower back off the ground would also qualify as partial suspension.
In full suspension the person is completely supported by suspension ropes, cables or chains, and they have no contact with the ground. The position of the person's body in a full suspension may be horizontal, vertical or inverted; it is only limited by their endurance and the skill of the binder.
A small group practise self-suspension.[50]
Rope and knots
editMetal can be used for bondage ties with handcuffs, metal hobbles and spreader bars. The rope used for Japanese bondage is made from natural fibres such as hemp, it is prepared by boiling to make it soft, but it is coarse and binds to itself: there is a lot of friction, so the knots hold fast.[15]
The two basic ties are the single-column tie, where the 'column' could be the end of a limb or an attachment point, and the double column tie which could be used to bind two limbs. They all start with a basic knot, and finish with securing the loose ends.[51]
Danger and safety precautions
editThere is basic advice on precautions to take at a BDSM session. This includes never leaving the bound subject alone, never performing under the influence of alcohol or drugs and always having shears available to cut the rope in case there is an emergency.[52]
- Restricting the blood flow. The symptoms are numbness, temperature drop and color change. This happens gradually and tissue damage takes place slowly; if noticed and acted upon quickly, permanent damage is unlikely.
- Most common is impaired venous return, as the veins are closest to the surface. The skin becomes red, then purple. This is avoided by the two finger rule; where the tie is loose enough for two fingers to be placed under the rope. This becomes dangerous around the head and around the male genitals.
- Impaired arterial flow, which is difficult to achieve, is more dangerous and results in the limb going white.[53]
- Nerve damage is more serious, happens very quickly, is cumulative and often irreversible. Bondage practitioners should know the position of the nerves and place their rope to avoid them. Symptoms are pain, numbness or loss of feeling.
- The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve in the leg and the radial nerve in the mid-upper arm area are common sites of nerve injury. The knees, elbows, groin, and armpits are places where major arteries, veins, and nerves are near the surface and should be subjected to only moderate pressure.[52]
- Asphyxiation is caused by restricting the airways round the neck and by compression of the lungs.[54]
- Suspension trauma leading to dizziness, nausea or fainting
- Impact injuries due to falling.[54]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Redmayne, Lazarus (17 December 2017). "About TheDuchy – TheDuchy". TheDuchy. Archived from the original on 30 April 2019. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n ASI (24 April 2019). "40+ Bondage Positions:The Restrained Elegance Lexicon of Slavegirl Positions". ASI BDSM. Archived from the original on 29 August 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- ^ "Elbow bondage". Informed Consent. Archived from the original on 20 November 2007.
- ^ Easternrope.com, retrieved on Aug 25, 2009 Archived February 6, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Positional Asphyxia". Archived from the original on 15 July 2013.
- ^ a b cee (3 May 2018). "Shibari 101: Let's Talk About Japanese Rope Bondage". Autostraddle. Archived from the original on 26 May 2019. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- ^ "Ebi ('Shrimp') Tie". TheDuchy. 10 December 2017. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 1 May 2019.
- ^ Harrington 2007, pp. 99–100.
- ^ Midori 2001, pp. 107–110.
- ^ Tatu (2005). "Glossary: Terms Related to Japanese Shibari / Kinbaku / Bondage". www.ds-arts.com. Archived from the original on 7 March 2019. Retrieved 2 March 2019.
- ^ Roos, Bob. "Ebizeme". RopeMarks. Archived from the original on 20 August 2019. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- ^ a b "Japanese Rope ARt - ibari - Kinbaku Tutorials - Nawa Dojo". www.japaneseropeart.com. Archived from the original on 31 May 2019. Retrieved 19 August 2019.
- ^ Roos, Bob. "Gyaku-ebi shibari". RopeMarks. Archived from the original on 21 August 2019. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- ^ a b Lazarus (10 December 2017). "Hishi Karada ('Rope Dress') – TheDuchy". The Duchy. Archived from the original on 29 August 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Hywel & Ariel. "The Restrained Elegance lexicon of slavegirl bondage poses and positions". Restrained Elegance. Archived from the original on 23 August 2017. Retrieved 25 August 2009.
- ^ Harrington 2007, pp. 125–145.
- ^ a b "Sukaranbo - Cherry Rope Bondage". Japanese-Rope-Bondage.com. Archived from the original on 22 February 2009. Retrieved 2 March 2019.
- ^ Harrington 2007, p. 210.
- ^ a b "Crotch Rope". Kinkly. 9 February 2022.
- ^ a b Redmayne, Lazarus (14 December 2017). "Tutorials – TheDuchy". TheDuchy. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ^ Russell, Diana (14 May 1998). Dangerous Relationships: Pornography, Misogyny And, Rape. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-7619-0525-7.
- ^ Redmayne, Lazarus (19 December 2017). "Unchastity Belt – TheDuchy". The Dutchy. Archived from the original on 25 October 2019. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ Aggrawal, Anil (2008). Forensic and Medico-legal Aspects of Sexual Crimes and Unusual Sexual Practices. CRC Press. p. 147. ISBN 9781420043099.
- ^ a b "Crash Restraint-Takate kote survey". crash-restraint.com. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 30 April 2019.
- ^ "Bondage Knowledge: Box Tie Arm Placement". The Black Pomegranate. 23 May 2016. Archived from the original on 30 April 2019. Retrieved 30 April 2019.
- ^ "Cross-Chest Box Tie". TheDuchy.com. 10 December 2017. Archived from the original on 30 April 2019. Retrieved 30 April 2019.
- ^ Redmayne, Lazarus (10 December 2017). "Star Harness (w Arms) – TheDuchy". Archived from the original on 24 September 2019. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ^ Redmayne, Lazarus (10 December 2017). "Pentagram – TheDuchy". The Duchy. Archived from the original on 24 September 2019. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- ^ "Breast Bondage". Kinkly. 1 May 2022.
- ^ a b c d Pinkerton, Martha (17 November 2022). "In-Depth Guide on How to Tie Tits". Joy Nights.
- ^ a b Lazarus (3 July 2018). "Shinju – TheDuchy". The Duchy. Archived from the original on 29 August 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- ^ Lazarus (17 December 2017). "Bikini Harness – TheDuchy". The Duchy. Archived from the original on 29 August 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- ^ Jamie (26 October 2022). "Breast Fetish: 9 Types of Breast Kinks". Kink Lovers.
- ^ a b c "What is Breast Bondage? Learn the Basics and Safety [NSFW]". Lovense. 22 August 2018. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ Harrington 2007, pp. 51–96.
- ^ Harrington 2007, p. 175.
- ^ a b Harrington 2007, p. 177.
- ^ a b "Wrists over Head to Back". crash-restraint.com. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2019.
- ^ Roos, Bob. "Teppo/Teppou shibari". RopeMarks. Archived from the original on 31 August 2019. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
- ^ Witold Fitz-Simon (2010). "Pashchima Namaskarasana (Reverse Prayer Pose)". Yoga Art and Science. Archived from the original on 25 March 2019. Retrieved 2 March 2019.
- ^ a b c Jay Wiseman's Erotic Bondage Handbook, Jay Wiseman, Greenery Press, 2000, ISBN 1-890159-13-1: subchapter "Hoods": pages 217-220
- ^ Graveris, ⭐ Dainis (8 June 2019). "Ball Gags 101: The Ultimate Guide To BDSM Gag & Bondage Play". Medium. Archived from the original on 2 September 2019. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- ^ "Bondage Position: Spreadeagle « Leather Cuffs and Silken Bonds". leathe rcuffs and silken bonds. Archived from the original on 1 September 2019. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- ^ "Beginner's Guide to the BDSM Cross - Make St. Andrew Blush". Lovense. 12 June 2019. Archived from the original on 13 September 2019. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- ^ Fetters. "Playroom & Furniture". www.fetters.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2 July 2019. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ Redmayne, Lazarus (20 July 2019). "Chair Tie – Legs-Up ③ –". TheDuchy. Archived from the original on 24 October 2019. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ Larocco, Matthew (2016). Submissive's Guide To BDSM Vol. 3: 89 Advanced Topics Every Sub Must Know Before Submissive Training. Enlightened Publishing. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- ^ Nawakari, Shin (1 May 2017). Essence of Shibari: Kinbaku and Japanese Rope Bondage. Mystic Productions Press. ISBN 9781942733874. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Joint (GFDL) and cc-by-sa 3.0 content. "Strapaddo Tie - BDSM Wiki". bdsmwiki.info. Archived from the original on 25 August 2019. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)There is the Creative Commons Attribution-Sharealike 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY-SA) and the GNU Free Documentation License (GFDL) clause on this wiki. - ^ a b Tiziano, Stephanos; Tiziano, Shay. "Suspension 101 – Stefanos and Shay". www.stefanosandshay.com. Archived from the original on 2 October 2019. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- ^ Harrington 2007, p. 44.
- ^ a b Tizianos, Stephanos; Tizianos, Shay (2019). "Introduction and basic risks – Remedial Ropes". Remedial rope. Archived from the original on 20 September 2019. Retrieved 20 September 2019.
- ^ Tizianos, Stephanos; Tizianos, Shay (2019). "Circulation – Remedial Ropes". Remedial rope. Retrieved 20 September 2019.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Tizianos, Stephanos; Tizianos, Shay (2019). "Positioning and Location – Remedial Ropes". Remedial rope. Archived from the original on 20 September 2019. Retrieved 20 September 2019.
Bibliography
edit- Harrington, Lee (2007). Shibari You Can Use: Japanese rope bondage and erotic macramé. Lynnwood, WA: Mystic Productions. ISBN 978-0-615-14490-0. OCLC 156813720.
- Midori (2001). The Seductive Art of Japanese Bondage. Greenery Press. ISBN 9781890159382.
- Rose, Chanta (2006). Bondage for Sex. BDSM Press. pp. 54–66, 96–103. ISBN 0-9777238-0-1.
- Trimmer, Eric J, ed. (1977). The Visual Dictionary of Sex. A & W Publishers. ISBN 0-89479-011-0.
- Two Knotty Boys (20 November 2006). Two Knotty Boys Showing You the Ropes. Green Candy Press. pp. 55–56. ISBN 978-1-931160-49-0.
- Wiseman, Jay (2000). Jay Wiseman's Erotic Bondage Handbook. Greenery Press. p. 259. ISBN 978-1-890159-13-9.
- Wiseman, Jay (1996). SM 101 (Second ed.). Greenery Press. pp. 134–137. ISBN 0-9639763-8-9.
External links
edit- Interview with Master K
- Hishi Karada how-to Archived 14 March 2019 at the Wayback Machine by Master Tatu
- Glossary of Japanese Bondage Terms - "See Karada" Archived 15 July 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Glossary explaining and showing the difference between hishi and kikkou styles
- Youtube videos, Fesselzeit showing a shrimp tie with overarm tie