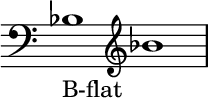
B♭ (B-flat), or, in some European countries, B, is the eleventh step of the Western chromatic scale (starting from C). It lies a diatonic semitone above A and a chromatic semitone below B,[1] thus being enharmonic to A♯, even though in some musical tunings, B♭ will have a different sounding pitch than A♯. B-flat is also enharmonic to C![]() (C-double flat).
(C-double flat).

When calculated in equal temperament with a reference of A above middle C as 440 Hz, the frequency of the B♭ above middle C is approximately 466.164 Hz.[2] See musical pitch for a discussion of historical variations in frequency.
While orchestras tune to an A provided by the oboist, wind ensembles usually tune to a B-flat.[3]
In Germany, Russia, Poland, Scandinavia and Slovakia this pitch is designated B, with 'H' used to designate the B-natural. Since the 1990s, B-flat is often denoted Bb or "Bess" instead of B in Swedish music textbooks. Natural B is called "B" by Swedish jazz and pop musicians, but still denoted H in classical music.[4] See B (musical note) and Note names and their history for explanations.
Designation by octave
edit| Scientific designation | Helmholtz designation | Octave name | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B♭−1 | B♭͵͵͵ or ͵͵͵B♭ or BBBB♭ | Subsubcontra | 14.568 |
| B♭0 | B♭͵͵ or ͵͵B♭ or BBB♭ | Subcontra | 29.135 |
| B♭1 | B♭͵ or ͵B♭ or BB♭ | Contra | 58.27 |
| B♭2 | B♭ | Great | 116.541 |
| B♭3 | b♭ | Small | 233.082 |
| B♭4 | b♭′ | One-lined | 466.164 |
| B♭5 | b♭′′ | Two-lined | 932.328 |
| B♭6 | b♭′′′ | Three-lined | 1864.655 |
| B♭7 | b♭′′′′ | Four-lined | 3729.31 |
| B♭8 | b♭′′′′′ | Five-lined | 7458.62 |
| B♭9 | b♭′′′′′′ | Six-lined | 14917.24 |
| B♭10 | b♭′′′′′′′ | Seven-lined | 29834.481 |
Scales
editCommon scales beginning on B♭
edit- B-flat major: B♭ C D E♭ F G A B♭
- B-flat natural minor: B♭ C D♭ E♭ F G♭ A♭ B♭
- B-flat harmonic minor: B♭ C D♭ E♭ F G♭ A B♭
- B-flat melodic minor ascending: B♭ C D♭ E♭ F G A B♭
- B-flat melodic minor descending: B♭ A♭ G♭ F E♭ D♭ C B♭
- B-flat Ionian: B♭ C D E♭ F G A B♭
- B-flat Dorian: B♭ C D♭ E♭ F G A♭ B♭
- B-flat Phrygian: B♭ C♭ D♭ E♭ F G♭ A♭ B♭
- B-flat Lydian: B♭ C D E F G A B♭
- B-flat Mixolydian: B♭ C D E♭ F G A♭ B♭
- B-flat Aeolian: B♭ C D♭ E♭ F G♭ A♭ B♭
- B-flat Locrian: B♭ C♭ D♭ E♭ F♭ G♭ A♭ B♭
- B-flat ascending melodic minor: B♭ C D♭ E♭ F G A B♭
- B-flat Dorian ♭2: B♭ C♭ D♭ E♭ F G A♭ B♭
- B-flat Lydian augmented: B♭ C D E F♯ G A B♭
- B-flat Lydian dominant: B♭ C D E F G A♭ B♭
- B-flat Mixolydian ♭6: B♭ C D E♭ F G♭ A♭ B♭
- B-flat Locrian ♮2: B♭ C D♭ E♭ F♭ G♭ A♭ B♭
- B-flat altered: B♭ C♭ D♭ E F♭ G♭ A♭ B♭
References
edit- ^ "B-flat (note) on Piano, Guitar, and Ukulele". Musicca. Retrieved 2024-01-18.
- ^ Suits, B. H. (1998). "Physics of Music Notes - Scales: Just vs Equal Temperament". MTU.edu. Michigan Technological University. Retrieved 5 February 2024.
- ^ "Why does the orchestra tune to the oboe?". Rockford Symphony Orchestra. Retrieved 2024-01-18.
- ^ Brian Blood. "Lesson 9 – Notes and Keys in Various Languages". Dolmetsch Online. Retrieved 15 July 2024.