The superior auricular muscle is a muscle above the auricle of the outer ear. It originates from the epicranial aponeurosis, and inserts into the upper part of the medial surface of the auricle. It draws the auricle upwards.
| Superior auricular muscle | |
|---|---|
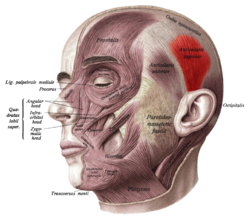 Face and neck muscles. Superior auricular muscle shown in red. | |
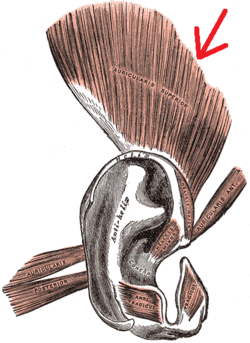 The muscles of the auricula. Superior auricular is at top (indicated by the red arrow). | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Temporal fascia |
| Insertion | Above the auricle of the outer ear |
| Artery | Posterior auricular artery |
| Nerve | Branches to auricular muscle from posterior auricular nerve of facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) |
| Actions | Pulls ear upward |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus auricularis superior |
| TA98 | A04.1.03.021 |
| TA2 | 2090 |
| FMA | 46855 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Structure
editThe superior auricular muscle originates from the epicranial aponeurosis.[1] Its fibres converge to be inserted by a thin, flattened tendon into the upper part of the medial surface of the auricle of the outer ear.[1]
It is the largest of the three auriculares muscles.[1] It is thin and fan-shaped.
Nerve supply
editThe superior auricular muscle is supplied by the temporal branch of the facial nerve (VII).[1][2]
Additional images
edit-
Auricula in context. Superior auricular shown in red.
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Auricularis superior muscles.
See also
editReferences
editThis article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1035 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d Barral, Jean-Pierre; Croibier, Alain (2009). "25 - Ear". Manual therapy for the cranial nerves. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone / Elsevier. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-3100-7.50028-8. ISBN 978-0-7020-3736-8. OCLC 460904284.
- ^ Rea, Paul (2016). "2 - Head". Essential clinically applied anatomy of the peripheral nervous system in the head and neck. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science. pp. 21–130. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803633-4.00002-8. ISBN 0-12-803664-8. OCLC 939866688.