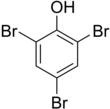
2,4,6-Tribromophenol (TBP) is a brominated derivative of phenol. It is used as a fungicide, as a wood preservative, and an intermediate in the preparation of flame retardants.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,6-Tribromophenol | |||
| Other names
Tribromophenol; 2,4,6-TBP; TBP
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.890 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H3Br3O | |||
| Molar mass | 330.801 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White needles or prisms[1] | ||
| Melting point | 95.5 °C (203.9 °F; 368.6 K)[1] | ||
| Boiling point | 244 °C (471 °F; 517 K)[3] 286 °C[1] | ||
| Slightly soluble[1] 59-61 mg/L[2] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  [4] [4]
| |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
2000 mg/kg (rat, oral)[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Production
editAlthough natural TBP has been identified in ocean sediments as a metabolite of marine fauna,[5] the commercial product is prepared industrially. In 2001, the production volume of TBP was estimated to be 2500 tonnes/year in Japan and 9500 tonnes/year worldwide.[2] TBP can be prepared by the controlled reaction of elemental bromine with phenol:[3]
Uses
editThe predominant use of TBP is as an intermediate in the preparation of flame retardants such as brominated epoxy resins.[2] TBP is reacted with sodium hydroxide to form the sodium salt, which is used as a fungicide and wood preservative.[6][7]
Bismuth salt
editThe bismuth salt is the active ingredient in Xeroform[clarification needed] dressing.[8]
Metabolism
editMicrobial metabolism in products treated with TBP is known to produce 2,4,6-tribromoanisole (TBA),[9] which has a musty odor. In 2010 and 2011, Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson voluntarily recalled some products due to TBA odors from wooden pallets which were treated with TBP.[10][11][12][13]
References
edit- ^ a b c d e "3851: Tribromophenol" in Gardner's Commercially Important Chemicals: Synonyms, Trade Names, and Properties, G. W. A. Milne (Editor), ISBN 978-0-471-73518-2, page 632
- ^ a b c Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 66: 2,4,6-Tribromophenol and Other Simple Brominated Phenols, International Programme on Chemical Safety
- ^ a b Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9526
- ^ Sigma-Aldrich Co., 2,4,6-Tribromophenol. Retrieved on 2015-02-19.
- ^ Fielman KT, Woodin SA, Lincoln DE (2001). "Polychaete indicator species as a source of natural halogenated organic compounds in marine sediments". Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 20 (4): 738–747. doi:10.1002/etc.5620200407. PMID 11345448. S2CID 42911887.
- ^ "2,4,6 Tribromophenol" (PDF). ICL Industrial Products. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 27, 2019. Retrieved April 13, 2022.
- ^ Tsunoda K, Takahashi M (1989). "Laboratory Evaluation of Chemicals as Wood Prerservatives: (1) Tribromophenol" (PDF). Wood Research. 76. Kyoto University: 39–48.
- ^ "MeSH Browser". meshb.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-27.
- ^ Frank B. Whitfield, Jodie L. Hill, Kevin J. Shaw (1997). "2,4,6-Tribromoanisole: a Potential Cause of Mustiness in Packaged Food". J. Agric. Food Chem. 45 (3): 889–893. doi:10.1021/jf960587u.
- ^ 38,000 more bottles of Lipitor recalled over odor complaints, CNN.com, October 30, 2010
- ^ Lipitor (atorvastatin) 40 mg: Recall Specific Bottles, drugs.com, Dec 23, 2010
- ^ Tylenol Recall Expands, WebMD Health News, January 18, 2010
- ^ McNeil Consumer Healthcare Announces Voluntary Recall Of One Product Lot Of TYLENOL Extra Strength Caplets 225 Count Distributed In The U.S.