164th Regiment (United States)
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2012) |
The 164th Regiment (Regional Training Institute) is a training unit of the North Dakota Army National Guard. As the 164th Infantry Regiment, it was formed during World War I, but traces its history to Dakota Territorial Militia units formed in the 1880s. The regiment was the first United States Army unit to land on Guadalcanal during World War II.
| 164th Regiment (Regional Training Institute) | |
|---|---|
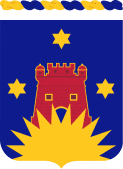 Coat of arms | |
| Active | 1885 |
| Country | |
| Branch | United States Army |
| Type | Regional Training Institute |
| Motto(s) | Je Suis Pret (I Am Ready) |
| Engagements | World War I World War II Korean War |
| Insignia | |
| DUI |  |
History
edit19th century
editThe 164th Infantry was originally organized as the 1st Infantry Regiment, Dakota Territorial Militia, in 1885. Upon the admission of North Dakota to the United States in 1889, the regiment was reorganized as the 1st Infantry Regiment, North Dakota National Guard. The regiment was mustered into federal service on 20 May 1898 for service in the Spanish-American War as the 1st North Dakota Volunteer Infantry, and was mustered out on 25 September 1899, resuming its state service.
World War I
editThe regiment entered federal service on 3 July 1916 for service on the Mexican border, and was stationed at Mercedes, Texas. On 14 February 1917, it was mustered out of service at Fort Snelling, Minnesota. On 5 August 1917, the 1st North Dakota was drafted into federal service, and assigned as an element of the 41st Division. On 4 October 1917, it was redesignated the 164th Infantry Regiment. The 41st Division went to France, but did not see combat and was broken up, with its personnel being reassigned as replacements to frontline units.
Interwar years
editThe 164th Infantry arrived at the port of New York on 17 February 1919 on the troopship USS President Grant and was demobilized on 28 February 1919 at Camp Dix, New Jersey. Per the National Defense Act of 1920, the 164th Infantry was reconstituted in the National Guard in 1921, assigned to the 34th Division, and allotted to the state of North Dakota. It was reorganized on 16 May 1923, with the regimental headquarters organized and federally recognized at Valley City, North Dakota. The headquarters was relocated on 14 December 1928 to Fargo, North Dakota. The regiment, or elements thereof, was called up to perform the following state duties: Company A performed martial law at a workers’ strike in Bismarck, North Dakota, 1–3 June 1933; Company A performed martial law in Bismarck during disputes over the gubernatorial accession, 17–24 July 1934. Company E was awarded the William Randolph Hearst National Marksmanship Trophy in 1934. The regiment conducted annual summer training most years at Camp Gilbert C. Grafton, Devils Lake, North Dakota, from 1921–39. For at least two years, in 1938 and 1939, the regiment also trained some 19 company-grade Organized Reserve infantry officers of the 88th Division at Camp Grafton. Colonel David S. Ritchie commanded the regiment from 16 May 1923–1 November 1928, while La Roy R. Baird, who later attained the rank of brigadier general, commanded the 164th Infantry from 1 November 1928 to October 1940. He was succeeded by Colonel Earl R. Sarles.[1][2]
World War II
editThe 164th Infantry entered federal service 10 February 1941. Before deployment overseas, the 164th was relieved from assignment to the 34th Infantry Division on 8 December 1941.
Commanded by Colonel Earle Sarles, the 164th transited the South Pacific ferry route in March 1942 to New Caledonia. There they joined the 182nd Infantry Regiment and the 132nd Infantry Regiment, in addition to artillery, engineer and other support units to form a new division on 24 May 1942, designated the Americal Division. The name Americal was derived from a combination of the words America and New Caledonia. The regiment spent nearly five months in combat training. In September, Colonel Sarles, a National Guard officer, was replaced as commander of the regiment by Colonel Bryant E. Moore, a West Point graduate. Moore would subsequently be promoted to command an infantry division in Europe, and the regiment would serve under other commanders, almost all of whom advanced to general's stars.[citation needed]
Arriving at Guadalcanal on 13 October 1942 ahead of its brother regiments as emergency reinforcement for the 1st Marine Division, the Regiment was the first U.S. Army unit to engage in offensive action during World War II in the Battle of Guadalcanal. Between 24 and 27 October, elements of the regiment withstood repeated assaults from Japanese battalions and inflicted some two thousand enemy casualties. The 1st Marine Division commander, Major General Alexander Vandegrift, was so impressed by the soldiers' stand that he issued a unit commendation to the regiment for having demonstrated "an overwhelming superiority over the enemy." In addition, the Marines took the unusual step of awarding Lt. Colonel Robert Hall, commander of the 3rd Battalion, 164th, with the Navy Cross for his role in these battles.[3]
Until the Americal Division commander, Major General Alexander M. Patch, and other units of the division arrived, the 164th fought alongside the Marines in a series of encounters with Japanese units in the Point Cruz area, where they successfully dislodged enemy troops from two hilltop strongpoints. The action earned them the nickname "The 164th Marines." Members of the 164th were also known as "jungle fighters" within the U.S. media because of the terrain on which they fought.
Later, the 164th participated in extensive jungle patrols as well as organized offensive sweeps of the island to eliminate remaining Japanese resistance. This experience gained the regiment valuable combat experience in jungle travel and navigation, ambush and counter-ambush, and small-unit tactics using small arms and light support weapons. After the Battle of Guadalcanal, the regiment returned to Fiji with the rest of the Americal Division to refit and replenish losses. At this point, many veteran officers and men of the 164th volunteered to join the 5307th Composite Unit, better known as Merrill's Marauders, for service in Burma.[4] With the rest of the Americal, the Regiment later participated in the Bougainville campaign, then fought to secure the islands of Leyte, Cebu, Negros, and Bohol, in the Philippines. The regiment was slated to be part of the invasion of Japan when the war ended in August.
Woodrow W. Keeble, the first Sioux Medal of Honor recipient, served with the 164th throughout the war. He was wounded several times and awarded the Purple Heart and multiple awards for valor during World War II. His Medal of Honor, officially recognized in 2008, came for his actions in the Korean War.[5]
Corporal Kenneth S. Foubert of the 164th Infantry has been recognized as the first U.S. Army soldier to die in combat after the attack on Pearl Harbor. As he landed on the beach on Guadalcanal, he was struck by shrapnel from a bomb dropped by a Japanese plane.
Inter war service
editThe 164th was inactivated 24 November 1945 at Fort Lawton, Washington. On 10 June 1946, the 164th Infantry was relieved from assignment to the Americal Division and assigned to the 47th Infantry Division.
On 1 May 1947, the 164th was reorganized and federally recognized 1 May 1947 as Company E of the 164th Infantry at Williston.
Korean War service
editThe 164th was ordered to federal service 16 January 1951 at Williston. Company C of the 164th Infantry (NGUS) organized and federally recognized 16 January 1953 at Williston while the 164th Infantry was on federal service.
The 164th was inactivated from active federal Service 2 December 1954 and reverted to state control and redesignated as Company C, 164th Infantry; federal recognition was concurrently withdrawn from Company C, 164th Infantry (NGUS).
Distinctive unit insignia
edit- Description
A gold color metal and enamel device 1+1⁄8 inches (2.9 cm) in height overall consisting of a shield blazoned: Azure, a Spanish castle Gules door of the first and fimbriated Or between three six-pointed mullets one and two and debruised in base by a demi-sun issuing from base of the last. Attached below the shield is a blue scroll inscribed "JE SUIS PRET" in gold.
- Symbolism
The service of the former organization, 142d Engineer Battalion, is indicated by the blue shield for Infantry, with the Spanish castle taken from the Spanish Campaign medal representing Spanish War service. The Philippine Insurrection service is indicated by the three mullets from the Philippine Island flag. The sun in base, from the 41st Division shoulder sleeve insignia, denotes World War I service with that division.
- Background
The distinctive unit insignia was originally approved for the 164th Regiment Infantry in 1933. It was redesignated for the 142d Engineer Battalion on 8 May 1956. On 26 December 1974 the insignia was rescinded (cancelled). The insignia was approved for the 164th Regiment, with description and symbolism revised, on 6 November 1997.
Coat of arms
editBlazon
edit- Shield
Azure, a Spanish castle Gules door of the first and fimbriated Or between three six-pointed mullets one and two and debruised in base by a demi-sun issuing from base of the last.
- Crest
That for the regiments and separate battalions of the North Dakota Army National Guard: From a wreath Or and Azure, a sheaf of three arrows Argent armed and flighted Gules behind a string bow fesswise Or with a grip of the second. Motto JE SUIS PRET (I Am Ready).
Symbolism
edit- Shield
The service of the former organization, 142d Engineer Battalion, is indicated by the blue shield for Infantry, with the Spanish castle taken from the Spanish Campaign medal representing Spanish War service. The Philippine Insurrection service is indicated by the three mullets from the Philippine Island flag. The sun in base, from the 41st Division shoulder sleeve insignia, denotes World War I service with that division.
- Crest
The crest is that of the North Dakota Army National Guard.
Background
editThe coat of arms was originally approved for the 164th Regiment Infantry on 11 an 1933. It was redesignated for the 142d Engineer Battalion on 8 May 1956. On 26 December 1974 the coat of arms was rescinded (cancelled). The coat of arms was approved for the 164th Regiment, with description and symbolism revised, on 6 November 1997.
Medal of Honor recipient link
editReferences
edit- ^ Clay, Steven E. (2010). U.S. Army Order of Battle, 1919-1941, Volume 1. The Arms: Major Commands and Infantry Organizations, 1919-41. Fort Leavenworth, KS: Combat Studies Institute Press. pp. 437–438. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ [1] Archived 29 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine Prairie Public Broadcasting » Dakota Datebook
- ^ Shoptaugh, Terry, They Were Ready: The 164th Infantry in the Pacific War, 164th Infantry Association, 2010.
- ^ George, John B. (Lt. Col), Shots Fired in Anger, NRA Press (1981), p. 420
- ^ https://www.army.mil/medalofhonor/keeble/profile/index.html Refer to U.S. Army records, Master Sergeant Woodrow Wilson Keeble
- ^ "U.S. Army Medal of Honor page for Woodrow Keeble". U.S. Army. Retrieved 9 January 2014.
Bibliography
edit- George, John B. (Lt. Col), Shots Fired in Anger, NRA Press (1981)
- Shoptaugh, Terry, They Were Ready: The 164th Infantry in the Pacific War, 164th Infantry Association, 2010.
Further reading
edit- Anderson, Charles R. Guadalcanal. The U.S. Army Campaigns of World War II. United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 72-8. Archived from the original on 20 December 2007. Retrieved 17 August 2010.
External links
edit- 164th Infantry web site
- 164th Infantry Association Records
- History Highlights – North Dakota National Guard
- Company K of the 164th Infantry Regiment – Dickinson Area Public Library
- 164th Infantry Regiment Photographs – Elwyn B. Robinson Department of Special Collections, Chester Fritz Library, University of North Dakota