The Île de Sein [il də sɛ̃] is a Breton island in the Atlantic Ocean, off Finistère, eight kilometres from the Pointe du Raz (raz meaning "water current"), from which it is separated by the Raz de Sein. Its Breton name is Enez-Sun. The island, with its neighbouring islets, forms the commune of Île-de-Sein in the Finistère department of Brittany in north-western France. Inhabitants of Île-de-Sein are called in French Sénans.
Île-de-Sein
Enez-Sun | |
|---|---|
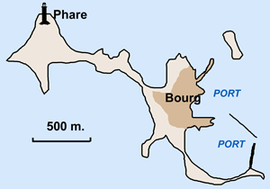 Close-up of the island | |
| Coordinates: 48°02′12″N 4°50′58″W / 48.0367°N 4.8494°W | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Brittany |
| Department | Finistère |
| Arrondissement | Quimper |
| Canton | Douarnenez |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Didier Fouquet[1] |
Area 1 | 0.58 km2 (0.22 sq mi) |
| Population (2019)[2] | 260 |
| • Density | 450/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 29083 /29990 |
| Elevation | 0–9 m (0–30 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
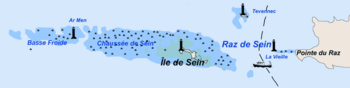


Lying on the sea routes going south from the English Channel, Sein is well known for the dangers of its waters, the Chaussée de Sein, a vast zone of reefs stretching more than 30 miles from east to west, requiring numerous lighthouses, beacons, and buoys. The lighthouses near the reef include Ar Men, La Vieille and Tévennec.
History
editThere are two megalithic menhirs on the island, which is flat and treeless.[3]
It is mentioned by the Roman geographer Pomponius Mela.[3]
The island women used to wear a black headdress, and in the past, they had a reputation for enticing sailors onto the rocks by witchcraft. In the past, it was also known for its wreckers.[4]
During World War II, German forces occupied the island. The Île de Sein lighthouse (Le Phare de Goulenez), built in 1839 at the north-western end was destroyed - it was later rebuilt in 1952. After hearing General de Gaulle's call to resistance during World War II in his appeal to the French on 18 June 1940, every male inhabitant aged between 14 and 54[citation needed] (or 60, according to the island's official website[5]) (variously totalled as 114 to 128[citation needed]) set sail in their fishing boats for Britain to join the Free French forces. For this, on 1 January 1946, the community was awarded the high honour of the Order of the Liberation.
During the 1960s, French artists Maurice Boitel and Jean Rigaud painted on the Île de Sein.
It is featured in the 1995 French film Élisa.
Geography
editClimate
editÎle de Sein has an oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification Cfb). The average annual temperature in Île de Sein is 12.9 °C (55.2 °F). The average annual rainfall is 815.0 mm (32.09 in) with December as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 17.8 °C (64.0 °F), and lowest in February, at around 8.4 °C (47.1 °F). The highest temperature ever recorded in Île de Sein was 32.3 °C (90.1 °F) on 11 July 1983; the coldest temperature ever recorded was −6.5 °C (20.3 °F) on 13 January 1987.
| Climate data for Île de Sein (1981–2010 averages, extremes 1977−2015) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.8 (62.2) |
16.0 (60.8) |
20.8 (69.4) |
26.5 (79.7) |
28.0 (82.4) |
28.0 (82.4) |
32.3 (90.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
27.8 (82.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
18.5 (65.3) |
16.8 (62.2) |
32.3 (90.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 10.6 (51.1) |
10.4 (50.7) |
12.0 (53.6) |
13.8 (56.8) |
16.5 (61.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
21.1 (70.0) |
21.0 (69.8) |
19.4 (66.9) |
16.3 (61.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
11.4 (52.5) |
15.4 (59.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 8.7 (47.7) |
8.4 (47.1) |
9.7 (49.5) |
11.1 (52.0) |
13.6 (56.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
17.6 (63.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
16.5 (61.7) |
14.2 (57.6) |
11.6 (52.9) |
9.6 (49.3) |
12.9 (55.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 6.9 (44.4) |
6.4 (43.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
8.4 (47.1) |
10.7 (51.3) |
12.8 (55.0) |
14.2 (57.6) |
14.5 (58.1) |
13.6 (56.5) |
12.2 (54.0) |
9.8 (49.6) |
7.7 (45.9) |
10.4 (50.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −6.5 (20.3) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
0.0 (32.0) |
1.8 (35.2) |
4.0 (39.2) |
6.2 (43.2) |
9.5 (49.1) |
8.2 (46.8) |
7.4 (45.3) |
4.6 (40.3) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 96.7 (3.81) |
77.9 (3.07) |
63.3 (2.49) |
59.6 (2.35) |
55.5 (2.19) |
36.0 (1.42) |
45.1 (1.78) |
43.7 (1.72) |
59.7 (2.35) |
85.0 (3.35) |
93.1 (3.67) |
99.4 (3.91) |
815.0 (32.09) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 15.0 | 12.7 | 12.1 | 11.1 | 9.3 | 7.1 | 6.9 | 8.2 | 8.5 | 12.9 | 14.6 | 15.2 | 133.5 |
| Source: Meteociel[6] | |||||||||||||
Legend
editAccording to Breton legend, Île de Sein was once home to a group of virgin druid priestesses called the Gallizenae. They are said to have had the power to predict the future, to calm the winds, and to take the forms of different animals.[7]
See also
editFurther reading
edit- Queffélec, Henri, Un recteur de l'île de Sein, Éditions Bartillat, Paris, 1999, ISBN 2841001210
References
edit- ^ "Répertoire national des élus: les maires". data.gouv.fr, Plateforme ouverte des données publiques françaises (in French). 2 December 2020.
- ^ Téléchargement du fichier d'ensemble des populations légales en 2019, INSEE
- ^ a b Graves, Robert (1961). The White Goddess. London: Faber & Faber. p. 111. ISBN 0-571-06961-4.
- ^ MacQuoid, Katharine Sarah (1880). Île de Sein is known for wreckers. (phrase search) – via Google Books.[full citation needed]
- ^ "Site officiel de l'ile de Sein". Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ "Normales et records pour Sein (29)". Meteociel. Retrieved 8 June 2022.
- ^ "Gallizenae - Oxford Reference". oxfordreference.com.
External links
editMedia related to Île de Sein at Wikimedia Commons
- Base Mérimée: Search for heritage in the commune, Ministère français de la Culture. (in French)
- (in French) State Lighthouse "la VIEILLE" dated April 19, 2009
- (in French) State Lighthouse "Enez-Sun" dated April 19, 2009
- île de Sein's dolphins on YouTube
- Having defied the Nazis,Islanders take on the sea 23. July.2012 The New York Times
- Mayors of Finistère Association (in French)